Understanding Netopia NAT Behavior C-187
AA
AA
pp
pp
pp
pp
ee
ee
nn
nn
dd
dd
ii
ii
xx
xx
CC
CC
UU
UU
nn
nn
dd
dd
ee
ee
rr
rr
ss
ss
tt
tt
aa
aa
nn
nn
dd
dd
ii
ii
nn
nn
gg
gg
NN
NN
ee
ee
tt
tt
oo
oo
pp
pp
ii
ii
aa
aa
NN
NN
AA
AA
TT
TT
BB
BB
ee
ee
hh
hh
aa
aa
vv
vv
ii
ii
oo
oo
rr
rr
This appendix describes how Network Address Translation (NAT) works within the Netopia R910. The Netopia
R910 implements a powerful feature called Network Address Translation as specified in RFC 1631. NAT is used
for IP address conservation and for security purposes since there will only be a single IP “presence” on the
WAN. This appendix describes the NAT functionality within the Netopia R910 and provides examples for setup
and use.
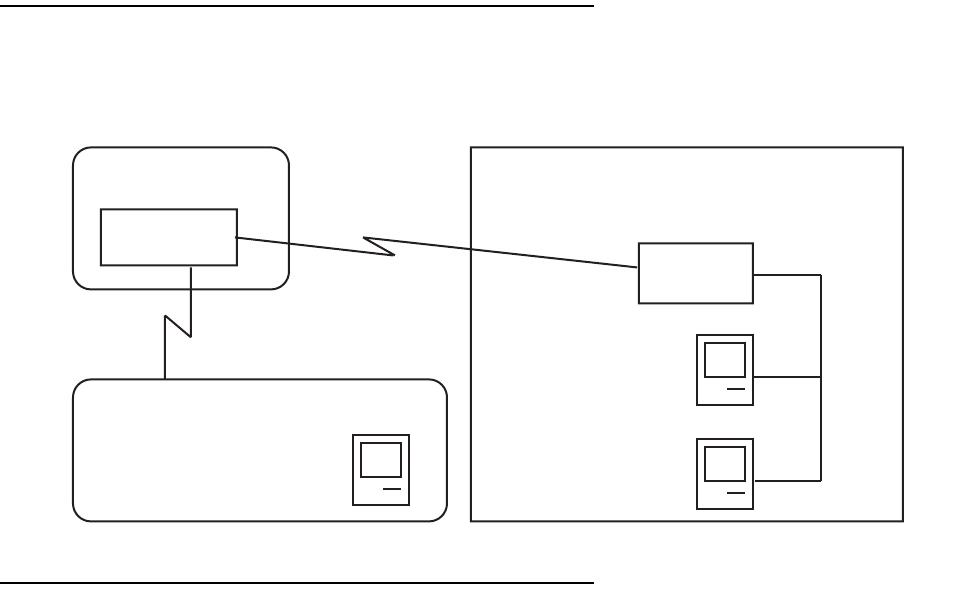
Network configuration
Below is a diagram of the network referenced in this appendix.
Background
NAT is a mechanism employed within the Netopia R910 to acquire a statically or dynamically assigned IP
address on its WAN interface and proxy against locally assigned IP addresses on its LAN interface. The Netopia
R910 uses a one-to-many IP address mapping scheme; that is against a single IP address the Netopia R910
acquires on its WAN interface, the Netopia R910 can proxy 14, 30, or an unlimited number of IP hosts on the
LAN interface.
In order to fully understand how NAT works, you must understand how a connection is established and IP
addresses are negotiated.
ISP Network Customer Site
Internet
Router
Netopia
LAN
Workstation B
IP: 192.168.5.3
Mask: 255.255.255.240
MAC: 00-05-02-00-1e-03
IP: 200.1.1.1
Mask: 255.255.255.0
Workstation A
IP: 192.168.5.2
Mask: 255.255.255.240
MAC: 00-05-02-04-12-4f
Netopia Router
WAN IP: 200.1.1.40
Mask: 255.255.255.0
MAC: 00-00-c5-60-21-0a
Netopia Router
LAN IP: 192.168.5.1
Mask: 255.255.255.240
MAC: 00-00-c5-60-21-0a
WWW Server
IP: 163.176.4.32
Mask: 255.255.255.0
MAC: 00-05-02-0c-1b-41


















