163
FINS/UDP Method Section 7-3
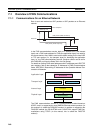
RSV (Reserved by
System)
Set to 00 (Hex).
GCT (Permissible Number
of Gateways)
Set to 02 (Hex).
DNA (Destination Network
Address)
Specifies the number of the network where the destination node is located.
The address can be specified in the following range.
00 (Hex): Local network
01 to 7F (Hex): Destination network address (1 to 127)
DA1 (Destination Node
Address
Specifies the number of the node where the command is being sent. This
node address is the address used for FINS, and is different from the IP
address used for Ethernet.
00 (Hex): Local PLC Unit
01 to FE (Hex): Destination node address (1 to 254)
FF (Hex): Broadcasting
When multiple Communications Units are mounted, DA1 specifies the node
address of the Unit connected to the network specified by DNA.
DA2 (Destination Unit
Address)
Specifies the number of the Unit at the destination node.
00 (Hex): PLC (CPU Unit)
10 to 1F (Hex): CPU Bus Unit unit numbers 0 to15 (16 to 31)
E1 (Hex): Inner Board
FE (Hex): Unit connected to network.
SNA (Source Network
Address)
Specifies the number of the network where the local node is located. The
ranges of numbers that can be specified are the same as for DNA.
SA1 (Source Node
Address)
Specifies the local node address. The ranges of numbers that can be speci-
fied are the same as for DA1.
SA1 (Source Unit
Address)
Specifies the number of the Unit at the local node.The ranges of numbers that
can be specified are the same as for DA2.
SID (Service ID) The SID is used to identify the process that data is sent from. Any number can
be set between 00 to FF hexadecimal for the SID. The same value set for the
SID in the command is returned by the node sending the response, allowing
commands and responses to be matched when commands are sent in suc-
cession to the same Unit.
7-3 FINS/UDP Method
7-3-1 Overview
FINS/UDP Features The FINS/UDP method is a FINS communications method that uses the UDP/
IP protocol. UDP/IP is a connectionless communications protocol. When a
message is sent from one node to another, the two nodes have an equal rela-
tionship and there is no clear connection. If using TCP is like making a tele-
phone call, then UDP is more like delivering a memo by hand. Although the
UDP protocol is fast, data communications are less reliable than with TCP.
In particular, when sending large amounts of data involving significant routing,
the user must program measures, such as retries, into applications in order to
improve reliability.