164
FINS/UDP Method Section 7-3
The FINS/UDP method has the following features:
• Because FINS/UDP is a connectionless protocol, there is no limit to the
number of corrections.
• FINS/UDP can be used for broadcasting.
• When data is sent via an IP network with multiple layers (such as the
Internet), communications reliability drops.
FINS/UDP Frame
Format
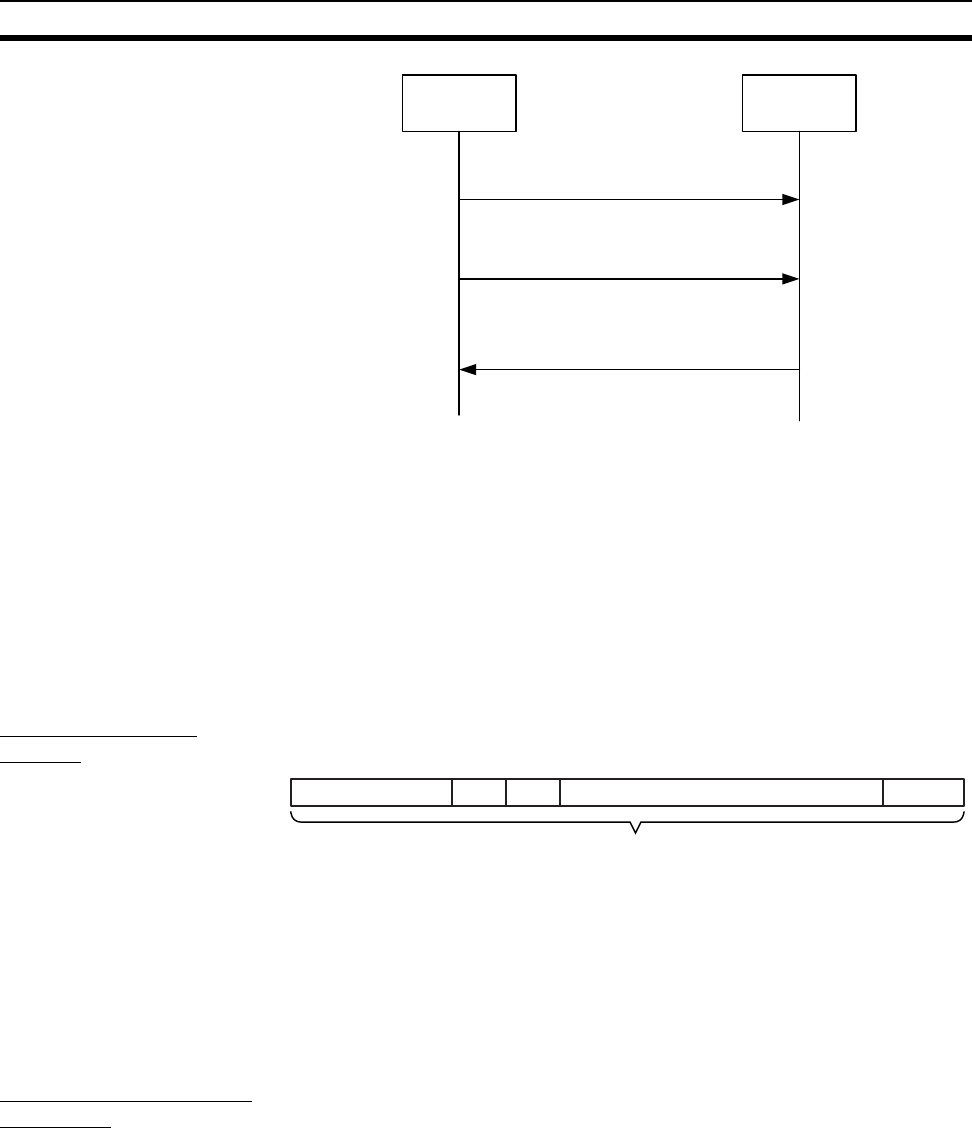
The following diagram shows the structure of a UDP packet used for sending
and receiving data on an Ethernet network.
As the diagram shows, a nested structure is used with the FINS/UDP method,
i.e., Ethernet Ver. 2, IP frame, UDP frame, and FINS frame. A UDP data sec-
tion (FINS frame) that exceeds 1,472 bytes is split into packets for transmis-
sion. The split UDP data is then joined automatically at the UDP/IP protocol
layer. There is normally no need to pay attention at the application layer to this
split, but it may not be possible to send 1,472-byte UDP packets over an IP
network with multiple layers. When using the FINS communications service in
a system such as this, select the FINS/TCP method.
UDP Port Numbers for
FINS/UDP
The UDP port number is the number for UDP to identify the application layer
(i.e., the FINS communications service in this case). When communications
are executed by UDP/IP, this port number must be allocated to the communi-
cations service.
The default setting for the FINS/UDP local UDP port number (i.e., the Ether-
net Unit's UDP port number) is 9600. To set another number, make the setting
for the FINS/UDP port using the Setup Tab in the Unit Setup.
At the Ethernet Unit, a UDP/IP frame received with a FINS/UDP port number
is recognized as a FINS frame.
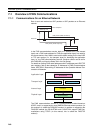
Node Node
Data transmission 1
Data transmission 2
Data transmission 3
Data is sent in one direction, with no
confirmation of whether the data was
received. Because there are few procedures
involved, data can be sent at high speed but
with less reliability than with TCP.
EthernetV.2 IP UDP FINS frame FCS
UDP packet