Quick Start
A Successful Connection
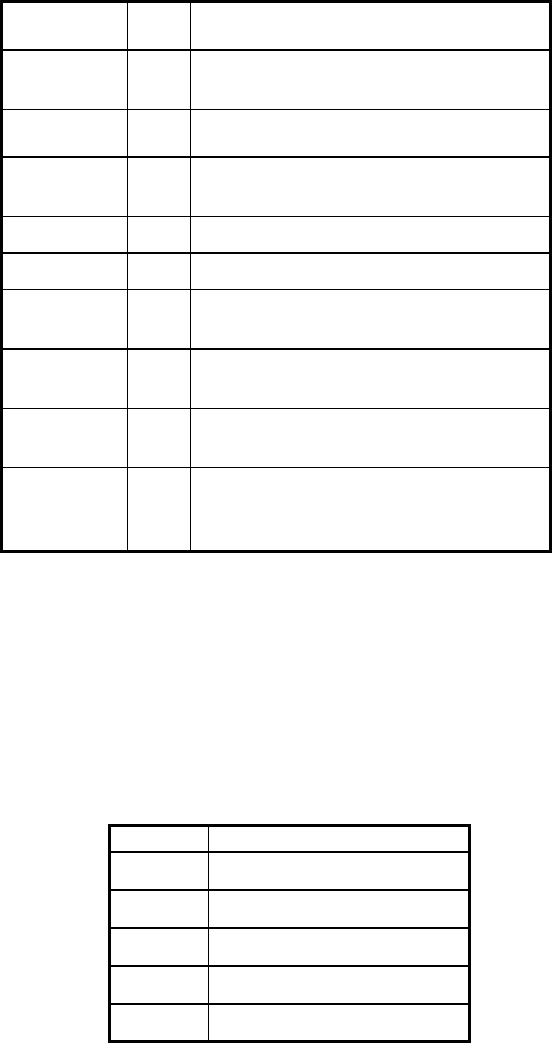
Table 2. ARIA demo operation modes
MODE HOT
KEY
DESCRIPTION
laser
l Displays the closest and furthest readings
from the robot’s laser range finder
io
i
Displays the state of the robot’s digital
and analog-to-digital I/O ports
position
p Displays the coordinates of the robot’s
position relative to its starting location
bumps
b Displays the status of the robot’s bumpers
sonar
s Displays the robot’s sonar readings
camera
c Controls and exercises the robot’s pan-
tilt-zoom robotic camera
gripper
g Controls, exercises, and displays status of
the robot’s Gripper
wander
w Sends the robot to move around at its own
whim, while avoiding obstacles
teleop
t Allows the user to drive and steer the
robot via the keyboard or a joystick
connected to the computer
ARIA prints out lots of diagnostic text as it negotiates a connection with the robot. If
successful, the client requests various AROS servers to start their activities, including sonar
polling, position integration, and
so on. The microcontroller
sounds an audible connection
cue, and you should hear the
robot’s sonar ping with a
distinctive and repetitive
clicking. In addition, the
motors-associated STATUS LED
on the User Control Panel should
light continuously (was flashing
slowly while awaiting
connection). Note that the
ARIA demo automatically
engages your robot’s motors
though a special client
command. Normally, the
motors are disengaged when
first connecting.
The amber SERIAL port
indicator LEDs on the robot’s
User Control Panel should blink
to indicate ARIA-client to AROS-
server communications, too.
OPERATING THE ARIA
D
EMONSTRATION CLIENT
When connected with the ARIA demo client, your robot becomes responsive and
intelligent. For example, it moves cautiously. Although it may drive toward an obstacle,
your ActivMedia robot will not crash because the ARIA demo includes obstacle-
avoidance behaviors which enable the robot to detect and actively avoid collisions.
The ARIA demo displays a menu of robot
operation options. The default mode of
operation is teleop. In teleop mode, you
drive the robot manually, using the arrow
keys on your keyboard or a joystick
connected to the client PC’s joystick port
(as opposed to a joystick port on the
robot).
Table 2. Keyboard teleoperation
KEY ACTION
↑
Increment forward velocity
↓
Decrement forward velocity
←
Incremental left turn
→
Incremental right turn
space All stop
While driving from the keyboard, each
keypress speeds the robot forward or
backward or incrementally changes its
direction incrementally. For instance, when turning, it is often useful to press the left- or
right-turn key rapidly several times in a row, because the turn increment is small.
The other modes of ARIA demo operation give you access to your robot’s various sensors
and accessories, including encoders, sonar, laser, Gripper, a pan-tilt-zoom robotic
camera, I/O port states, bumpers, and more. Accordingly, use the ARIA demo not only
26


















