15
Introduction
One of the key features of DAT is a technique known as Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT is an Internet
standard that allows a device (like the AP-2500) to use a single public IP address to provide Internet connectivity to
multiple devices (which would otherwise each need to have its own public IP address to communicate with the
network). The AP-2500 uses NAT for clients that are configured to obtain an IP address automatically from a DHCP
server (which is the typical configuration for hotspot users) and for clients with “misconfigured” static IP addresses (that
is, addresses that are not valid on the AP’s local IP network).
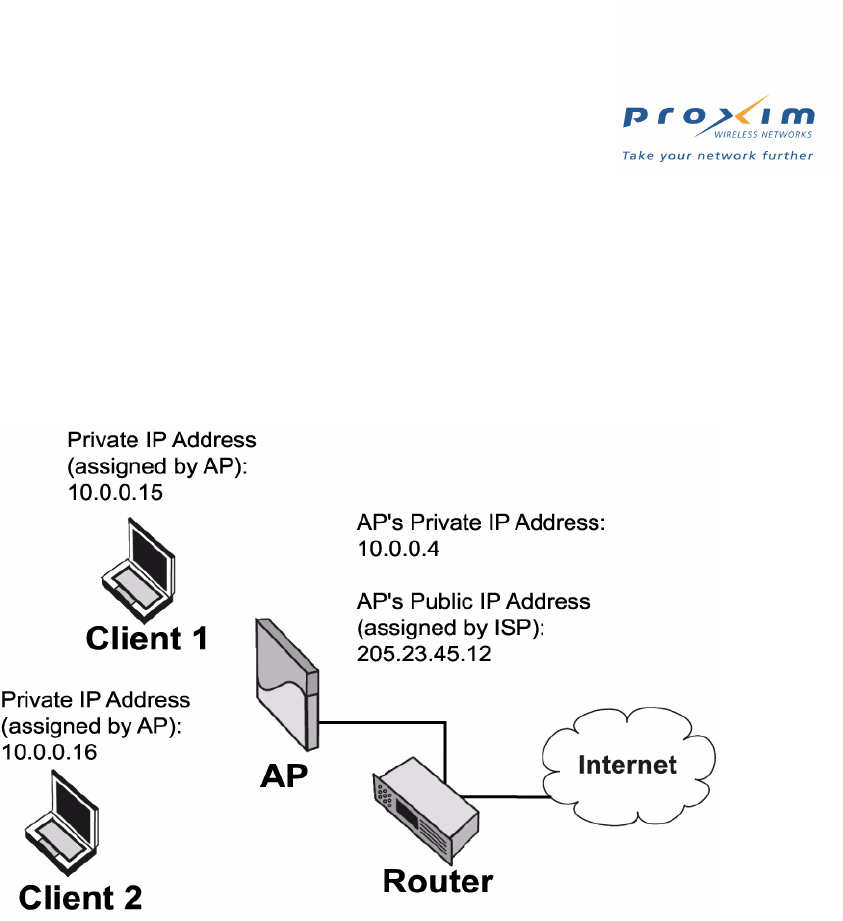
When performing NAT, an AP-2500 uses two IP addresses. One IP address is assigned by your ISP and is valid on the
Internet. This is known as a public or routable IP address. In the illustration below, the AP is assigned a public IP
address of 205.23.45.12.
Figure 1-1 The AP-2500 and NAT
The second IP address assigned to the AP is its private IP Address. This address is not valid on the Internet. The
Internet community has reserved several address ranges for private networks, including 10.0.0.0 and 192.168.0.0. By
default, the AP assigns itself a private IP address of 10.0.0.4. It also acts as a DHCP server to assign IP address in
that same private IP range to wireless subscribers. As shown in the illustration, the AP has assigned one client an IP
address of 10.0.0.15 and a second client an IP address of 10.0.0.16.
When the AP receives traffic from Client 1, it modifies the packet header so Client 1’s private IP address (10.0.0.15)
becomes the AP’s public IP address (205.23.45.12). Likewise, the AP performs the same function for traffic from
Client 2.
The AP differentiates between its clients by specifying different UDP and TCP port numbers for traffic that originates
from different clients. When the AP receives traffic from the Internet, the AP can determine to which client the traffic is
intended based on the port numbers in use.
The NAT technique used by the AP-2500 is known by many names including many-to-one NAT (that is, many private
IP addresses mapped to one public IP address) and Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) (due to the AP’s use
of port numbers to differentiate clients). For more information on NAT, see RFC 3022 at http://www.rfc-editor.org/.


















