3 – Planning
Device Access
3-12 59021-07 A
D
The following examples illustrate how to configure a security database.
3.4.5.1
Security Example: Switches and HBAs
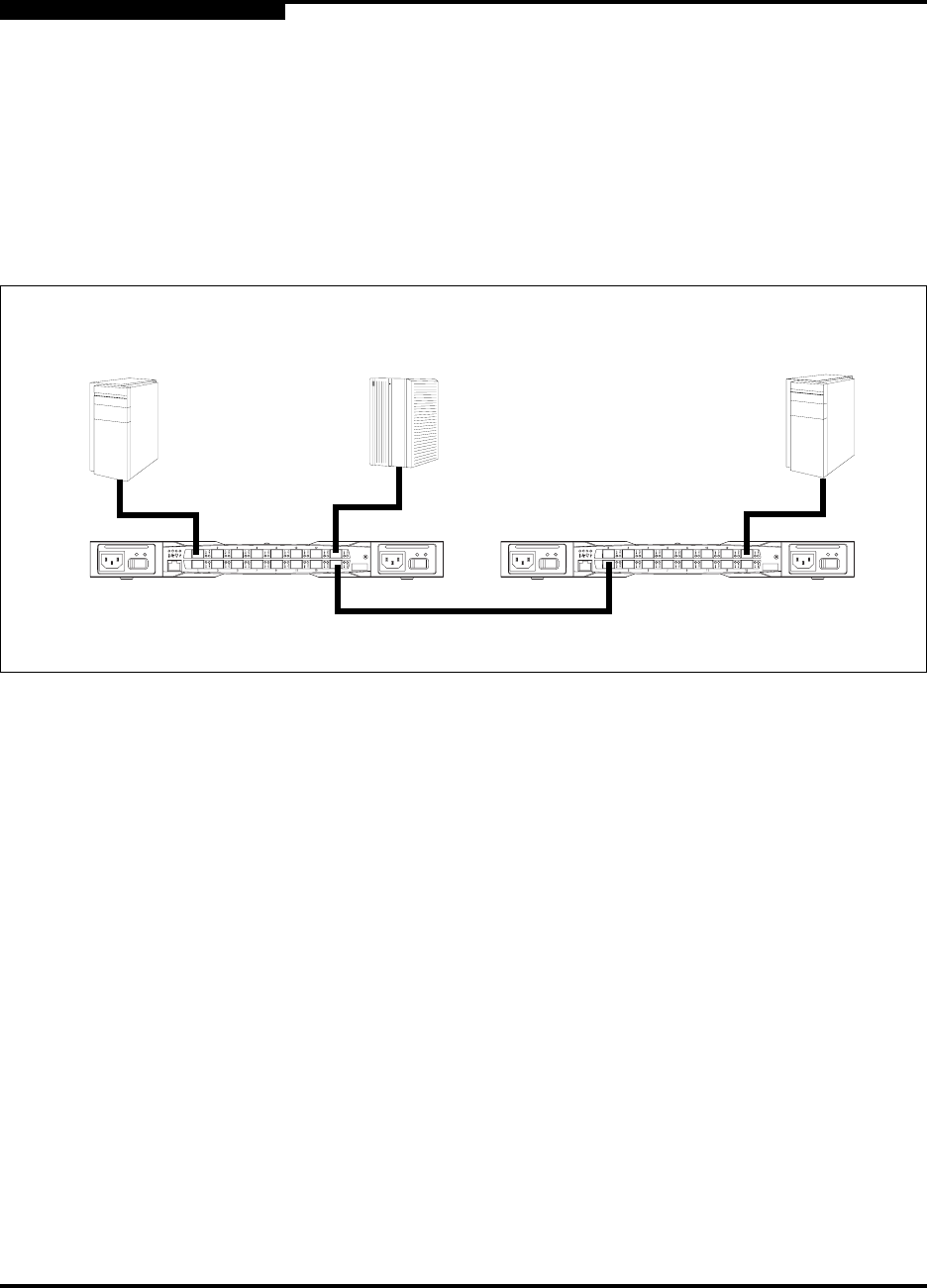
Consider the fabric shown in Figure 3-4. In this fabric, Switch_1 and HBA_1
support security while the JBOD, Switch_2 and HBA_2 do not. The objective is to
secure F_Ports and E_Ports in the fabric. To do this, configure security on the
devices that support security: Switch_1 and HBA_1.
Figure 3-4. Security Example: Switches and HBAs
1. Create a security set (Security_Set_1) on Switch_1.
2. Create a port group (Group_Port) in Security_Set_1 with Switch_1, and
HBA_1 as members. Because the JBOD is a loop device, it is excluded from
the port group.
You must specify HBAs by node worldwide name. Switches can be
specified by port or node worldwide name. The type of switch
worldwide name you use in the switch security database must be the
same as that in the HBA security database. For example, if you specify
a switch with a port worldwide name in the switch security database,
you must also specify that switch in the HBA security database with the
same port worldwide name.
For CHAP authentication, create 32-character secrets. The switch
secret must be shared with the HBA security database.
Device: Switch_1
WWN: 10:00:00:c0:dd:07:e3:4c
Security: Yes
Device: Switch_2
WWN: 10:00:00:c0:dd:07:e3:4e
Security: No
Device: HBA_1
WWN: 10:00:00:c0:dd:07:c3:4d
Security: Yes
Device: HBA_2
Security: No
E_Port
F_Port
F_Port
FL_Port
Device: JBOD
Security: No


















