5 – Managing Ports
Configuring Ports
59097-01 A 5-13
0
5.2.3
Changing Port Types
The ports can be configured to self-discover the proper type to match the device
or switch to which it is connected. Table 5-9 describes the port types.
To change the port type, do the following:
1. Select one or more ports in the faceplate display.
2. Open the Port menu and select Port Properties 1G/2G or Port Properties
10G to open the Port Properties dialog.
3. Click the Port Type radio button for the port type you want.
4. Click the OK button to write the new port type to the switch.
5.2.4
I/O Stream Guard
The I/O Stream Guard feature suppresses the Registered State Change
Notification (RSCN) messages on a port basis. I/O Stream Guard should be
enabled only on ports connected to initiator devices. To configure the I/O Stream
Guard option using the Port Properties dialog, open the Port menu, and select
Port Properties. Click the radio button that corresponds to one of the following:
Enable: Suppresses the reception of RSCN messages from other ports for
which I/O Stream Guard is enabled.
Disable: Allows free transmission and reception of RSCN messages.
Auto: Suppresses the reception of RSCN messages when the port is
connected to an initiator device with a QLogic HBA. For older QLogic HBAs,
such as the QLA2200, Device Scan must be enabled. The default is Auto.
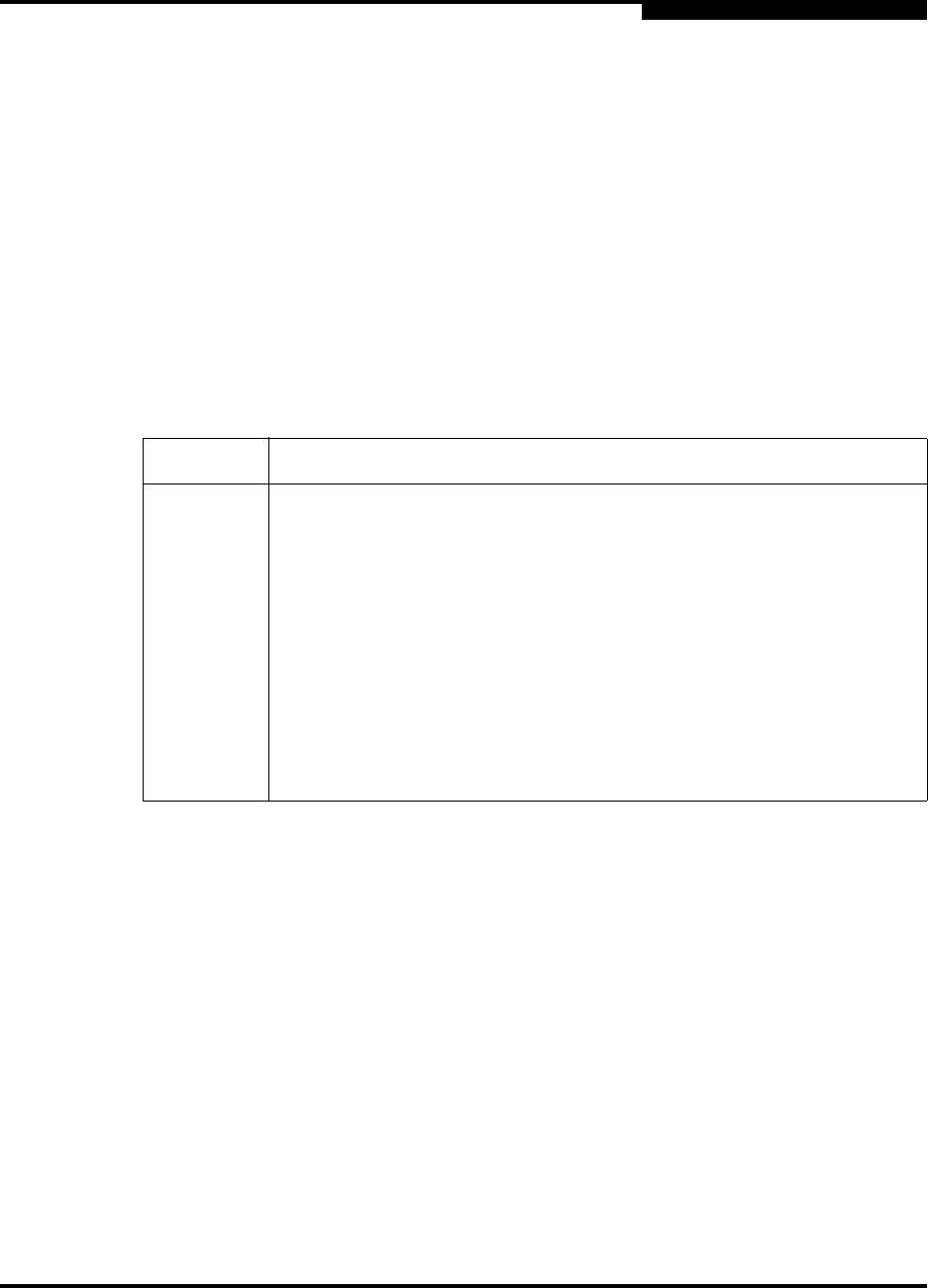
Table 5-9. Port Types
State Description
F_Port Fabric port - Supports a single public device (N_Port).
FL_Port Fabric loop port - Self discovers a single device (N_Port) or a loop of up
to 126 public devices (NL_Port). 1-Gbps/2-Gbps only.
G_Port Generic port - Self discovers as an F_Port or an E_Port.
GL_Port Generic loop port - Self discovers as an F_Port, FL_Port, or an E_Port.
GL_Port is the default port type. A single device on a public loop will
attempt to configure as an F_Port first, then if that fails, as an FL_Port.
1-Gbps/2-Gbps/4-Gbps only.
Donor Donor port - Allows buffer credits to be used by another port.
1-Gbps/2-Gbps/4-Gbps only.


















