Configuring a complex inter-VRF solution
Page 44 | Configure VRF-lite
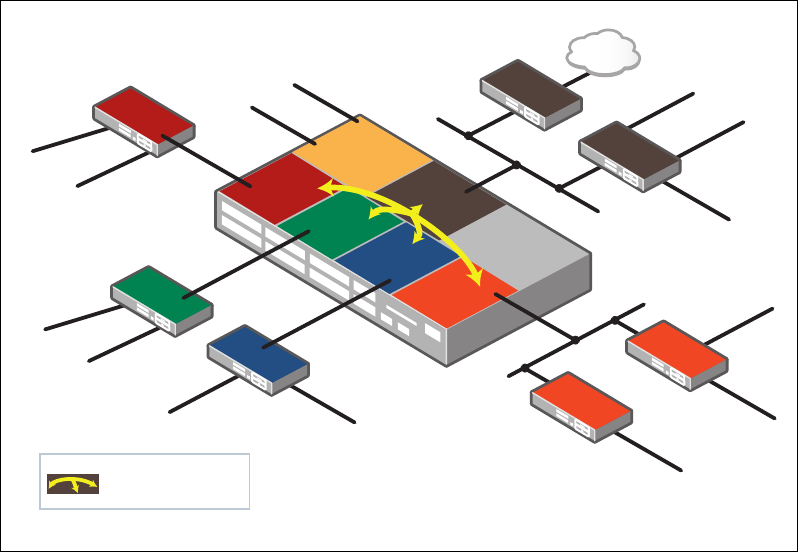
Configuring a complex inter-VRF solution
A network comprising of multiple devices that demonstrates inter-VRF routing. A variety of
routing protocols are used in this example.
Network description
VRF overlap
L06=6.6.6.6
VRF red
L01=1.1.1.1
OSPF-1
VRF green
L02=2.2.2.2
i-BGP
VRF blue
L03=3.3.3.3
RIP
VRF orange
L04=4.4.4.4
OSPF-2
VRF shared
L05=5.5.5.5
e-BGP
VRF-aware
device
i-BGP peer
router
RIP peer
router
OSFP peer
router
orange
router
shared
router
e-BGP
Internet
peer router
192.168.13.0/24
192.168.14.0/24
Internet
vlan 1
192.168.10.0/24
vlan 2
192.168.20.0/24
OSFP peer
router
vlan 7
192.168.50.0/24
vlan 6
192.168.10.0/24
vlan 5
192.168.100.0/24
192.168.15.0/24
192.168.16.0/24
vlan 3
192.168.30.0/24
192.168.17.0/24
192.168.18.0/24
vlan 4
192.168.40.0/24
192.168.19.0/24
192.168.20.0/24
192.168.140.0/24
192.168.43.0/24
192.168.44.0/24
192.168.45.0/24
Red type
- over lapping IP address ranges
- Inter VRF (IVR) communications
via Route leakage
The VRF-aware device has six separate VRFs configured, they are named: red, green, blue,
orange, shared and overlap. The VRF-aware device has static routes to two router networks
(orange router and shared router). It also peers to two OSPF routers (OSPF red peer and
OSPF orange peer), one i-BGP peer (i-BGP green peer) and one RIPv2 peer (RIP blue peer),
and one e-BGP peer (e-BGP shared Internet peer) that allows Internet access. None of the
peer devices are VRF aware. Dynamic inter-VRF communication allows selected VRFs to
access a common shared Internet connection.
Each VLAN(s) is associated with a VRF instance.
Each VRF instance also has its own unique IP local interface and associated local IP address.
Each VRF contains its own separate IP routing domain and separate (OSPF) routing
protocol instance or (BGP/RIP) address-family.
The VRF instances red, green, blue, and orange, are
all able to access the Internet via VRF
shared. They also have filtered access to ‘shared router’ subnets. All inter-VRF communication
between VRFs red, green, blue, and orange is blocked.
BGP, route-maps, and Access Control Lists (ACLs) are used to ‘leak’ selected routes between
VRFs to allow filtered inter-VRF (IVR) communication.


















