Features of AUDIX
37
Overview for Avaya IP600 Internet Protocol Communications Server
555-233-001 — Issue 5 — November 2000
4
Outgoing mailbox The outgoing section of a mailbox stores messages that users create, send, or forward.
In most cases, messages remain in the outgoing section until delivered. Table 5
describes the outgoing mailbox categories listed in default order. The AUDIX
administrator can change this order.
TCP/IP
AUDIX Transmission Control Program/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) provides the
ability to exchange messages with subscribers on other AUDIX systems. The remote
system can be next to or geographically distant from the local Avaya IP600 system.
AUDIX TCP/IP uses the proprietary AUDIX digital protocol to exchange messages,
user profiles, and message-status information with other machines. The digital
protocol uses a digital file format, similar to a data-file transfer between two
computer systems, to transmit the information. Digitally transmitted messages are
communicated quickly and with excellent sound quality.
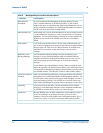
Table 5. Outgoing mailbox categories
Category Description
Filed Messages that users create and save in the outgoing section of a mailbox. Users
can later access these messages to modify them, address and send them again,
or delete them.
Undelivered Messages that have not been sent or messages scheduled for delivery at a
future date or time. Users can review, change, or cancel messages and their
addresses at any time before delivery.
Nondelivered Messages that AUDIX could not deliver. The application attempts to deliver a
message 10 times (or the administered number of times), then places the
message in this category. This usually indicates that the intended recipient’s
incoming mailbox is full, that the recipient’s application cannot recognize or
accept a message component (for example, is not fax-enabled), or that there
were transmission problems (for example, with an AMIS analog line).
Nondeliverable Messages defined as “nondeliverable” can be rescheduled for delivery with a
new address, or altered to allow forwarding, if needed.
Delivered Message headers that identify messages delivered but not yet listened to or that
identify messages containing nondeliverable components. The latter type of
message header is an Incomplete Delivery header. For example, if a message
contains more than the four components allowable (that is, a voice, fax, text,
and file attachment), the additional components are not delivered, and the
message header indicates that a component was not delivered.
Accessed Message headers that identify messages that have been listened to. A message
is considered accessed even if only the header has been listened to.