Chapter 4 Avaya P460 Layer 2 Features
LAG Configuration
LAG Overview
A LAG uses multiple ports to create a high bandwidth connection with another
device. For example, assigning four 100BASE-T ports to a LAG on an M4648ML-T
I/O module, allows the module to communicate at an effective rate of 400 Mbps
with another switch.
LAGs provide a cost-effective method for creating a high bandwidth connection.
LAGs also provide built-in redundancy for the ports that belong to a LAG. If a port
in a LAG fails, another port in the LAG handles its traffic .
To create a LAG, you must select a base port. The behavior of the LAG is derived
from the base port. The attributes of the base port, such as port speed, VLAN
number, etc., are applied to the other ports in the LAG.
When created, each LAG is automatically assigned a logical port number. You can
then use this logical port number for all configuration required for the LAG, such as
Spanning Tree, Redundancy, and so on.
Configuring LAGs
L You can only create LAGs by combining the same port types on the same I/O
Module.
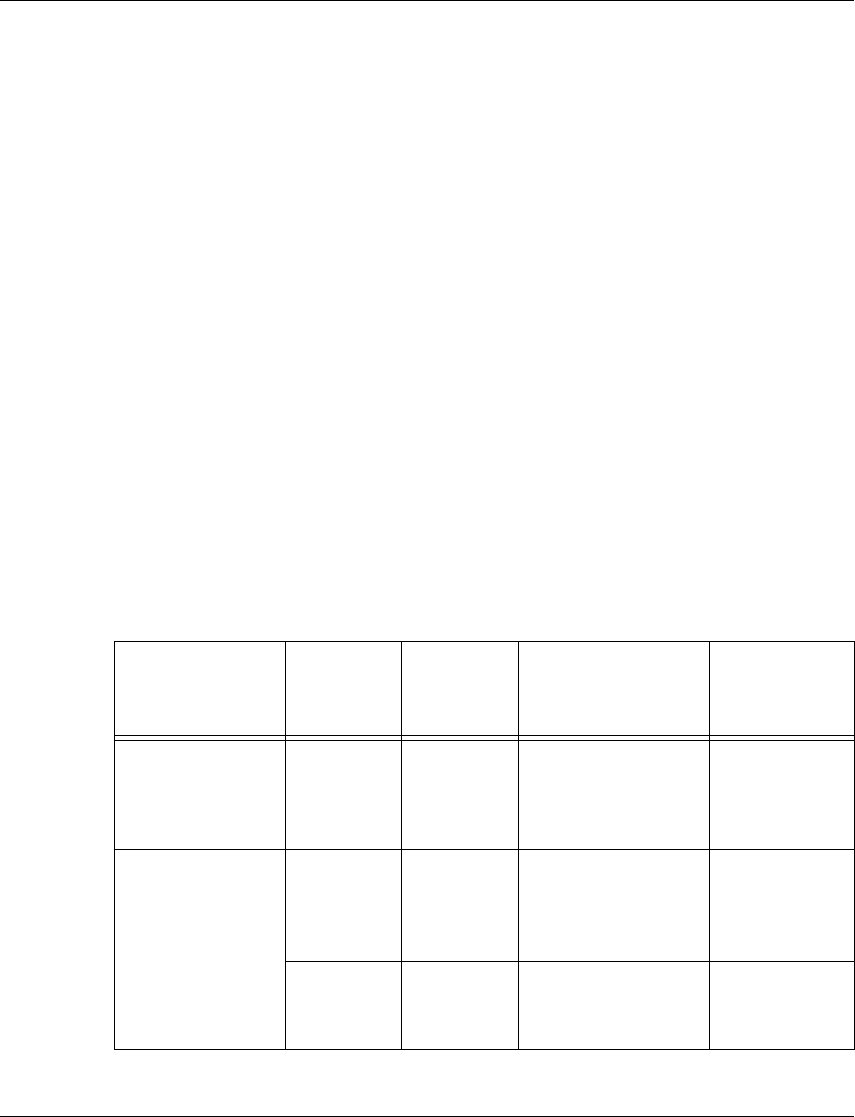
L Table 3.1 summarizes possible LAG configurations:
Table 4.1 Possible LAG Configurations
Module Maximum
number of
LAGs
Base port
is...
Additional ports
must be...
Logical port
numbers
M4648ML-T 6 10/100
Mbps
10/100 Mbps
Part of the same
group of 24 ports
(1-24; 25-28)
101-103
(ports 1-24)
104-106
(ports 25-48)
M4648ML-T-2G 6 10/100
Mbps
10/100 Mbps
Part of the same
group of 24 ports
(1-24; 25-28)
101-103
(ports 1-24)
104-106
(ports 25-48)
1 GBIC GBIC
On same the
module
107
28 Avaya P460 Configuration Guide


















