86
SmartStack STS16-20D/STS16-20R Token Ring Switches Installation and User Guide Switch Configuration
VLAN Configuration
The Virtual LAN feature can be used to partition a SmartStack STS16-20D/STS16-
20R or a stack of switches into several Virtual LANs, each containing its own set
of ports (the terms
Virtual LAN
and
domain
are interchangeable). Packets are
forwarded only between ports belonging to the same VLAN. The benefit of Virtual
LAN is to restrict access from one segment to another, either for security purposes
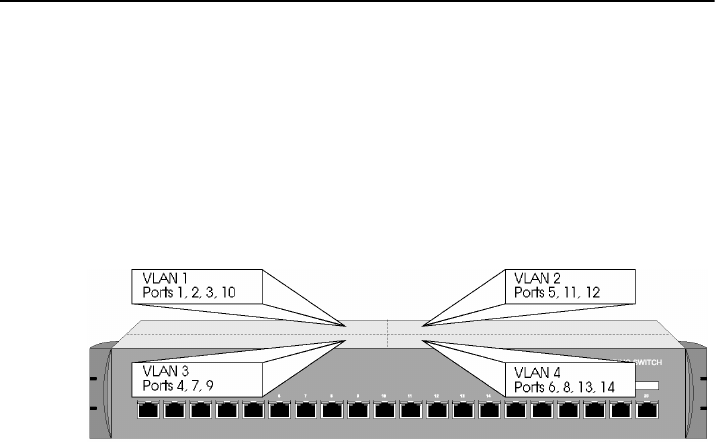
or to reduce intersegment (such as broadcast) traffic. Figure 25 illustrates a switch
with four VLANs.
Figure 25. SmartStack STS16-20D/STS16-20R with four VLANs
To set up domains using the VLAN Configuration menu, specify the ports
belonging to the domains, then set up the IP configurations, trap configuration (trap
receivers are associated with a set of VLANs and a receiver IP address) and STP
configurations specific to the appropriate VLANs. If you have already supplied
configuration information using the main configuration menus, that information
applies to VLAN “default”. Virtual LANs affects other SmartStack STS16-20D/
STS16-20R features in the following ways:
•
Spanning tree protocol (STP).
If you are using STP in a certain domain, you
must supply STP information for that domain. The STP software treats ports
on other domains as nonexistent. Domains do not affect port priorities and port
costs. You set these parameters using the STP Configuration menu that you
select from the main
Configuration
menu. Note that all BRFs defined in a
switch use the same STP bridge identifier. This means that BRFs from the
same switch or stack of switches cannot participate in the same spanning tree.
In other words, the spanning tree protocol will not work properly if VLANs are
connected.
•
SNMP trap tables.
Each domain appears to the network management system
as a physically different Token Ring switch unit. Certain MIB II objects and
proprietary objects are domain-sensitive, while others are not. For a list of
domain-sensitive objects, see Chapter 7, “Monitoring the Network from the
Console Statistics Menu”.


















