20
Obtaining a preferred projected image size
The distance from the projector lens to the screen, and the video format each factors in the projected
image size.
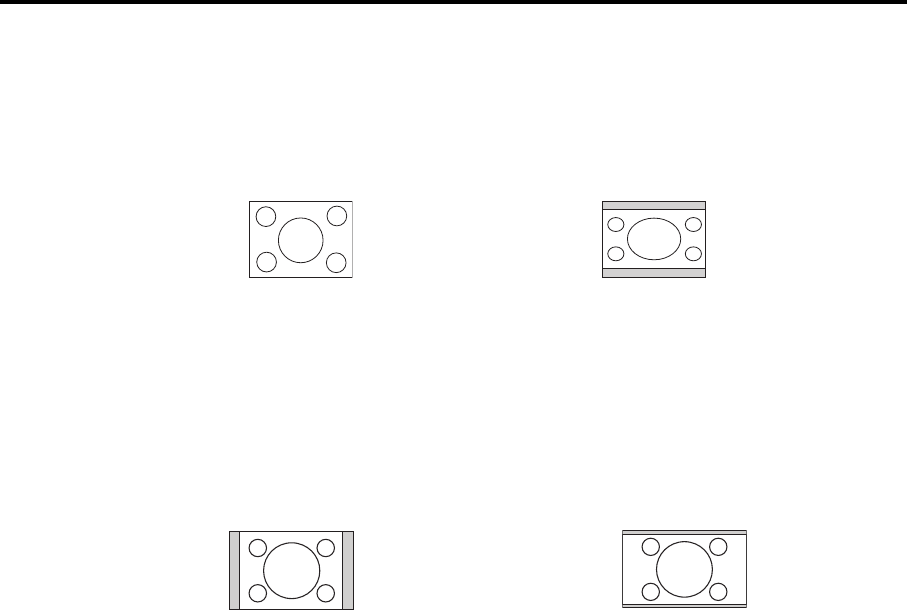
4:3 is the native aspect ratio of LV-X300ST. To be able to project a complete 16:9 (widescreen) aspect
ratio image, the projector can resize and scale a widescreen image to the projector's native aspect width.
This will result in a proportionally smaller height equivalent to 75% of the projector's native aspect height.
Thus, a 16:9 aspect image will not utilize 25% of the height of a 4:3 aspect image displayed by this
projector. This will be seen as darkened (unlit) bars along the top and bottom (vertical 12.5% height
respectively) of the 4:3 projection display area whenever displaying a scaled 16:9 aspect image in the
vertical center of the 4:3 projection display area.
16:10 is the native aspect ratio of LV-WX300ST. To be able to project a complete 16:9 (widescreen)
aspect ratio image, the projector can resize and scale a widescreen image to the projector's native aspect
width. This will result in a proportionally smaller height equivalent to 90% of the projector's native aspect
height.
Thus, a 16:9 aspect image will not utilize 10% of the height of a 16:10 aspect image displayed by this
projector. This will be seen as darkened (unlit) bars along the top and bottom (vertical 5% height
respectively) of the 16:10 projection display area whenever displaying a scaled 16:9 aspect image in the
vertical center of the 16:10 projection display area.
The projector should always be placed horizontally level (like flat on a table), and positioned directly
perpendicular (90° right-angle square) to the horizontal center of the screen. This prevents image
distortion caused by angled projections (or projecting onto angled surfaces).
The modern digital projector does not project directly forward (like older style reel-to-reel film projectors
did). Instead, digital projectors are designed to project at a slightly upward angle above the horizontal
plane of the projector. This is so that they can be readily placed on a table and will project forward and
upwards onto a screen positioned so that the bottom edge of the screen is above the level of the table (and
everyone in the room can see the screen).
You can see from the diagram on page 22, that this type of projection causes the bottom edge of the
projected image to be vertically offset from the horizontal plane of the projector.
If the projector is positioned further away from the screen, the projected image size increases, and the
vertical offset also increases proportionately.
When determining the position of the screen and projector, you will need to account for both the projected
image size and the vertical offset dimension, which are directly proportional to the projection distance.
When fine streaks are seen on projected images
This is due to interference with the screen surface and is not a mal-function. Replace the screen or
displace the focus a little.
4:3 aspect image in a 4:3 aspect display
area
16:9 aspect image scaled to a 4:3 aspect
display area
4:3 aspect image in a 16:10 aspect display area 16:9 aspect image scaled to a 16:10 aspect
display area


















