8-6
Cisco ONS 15310-CL and Cisco ONS 15310-MA Ethernet Card Software Feature and Configuration Guide R8.5
78-18133-01
Chapter 8 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling on the ML-Series Card
Understanding VLAN-Transparent and VLAN-Specific Services
bridge-group 40
Example 8-2 ML_Series B Configuration
no ip routing
bridge 30 protocol ieee
bridge 40 protocol ieee
!
!
interface FastEthernet0
no ip routing
mode dot1q-tunnel
bridge-group 30
!
interface FastEthernet1
mode dot1q-tunnel
bridge-group 40
!
interface POS0
!
interface POS0.1
encapsulation dot1Q 30
bridge-group 30
!
interface POS0.2
encapsulation dot1Q 40
bridge-group 40
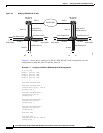
Understanding VLAN-Transparent and VLAN-Specific Services
The ML-Series card supports combining VLAN-transparent services and one or more VLAN-specific
services on the same port. All of these VLAN-transparent and VLAN-specific services can be
point-to-point or multipoint-to-multipoint.
This allows a service provider to combine a VLAN-transparent service, such as IEEE 802.1Q tunneling
(QinQ), with VLAN-specific services, such as bridging specific VLANs, on the same customer port. For
example, one customer VLAN can connect to Internet access and the other customer VLANs can be
tunneled over a single provider VLAN to another customer site, all over a single port at each site.
Table 8-1 outlines the differences between VLAN-transparent and VLAN-specific services.
Note VLAN-transparent service is also referred to as Ethernet Wire Service (EWS). VLAN-specific service
is also referred to as QinQ tunneling trunk UNI in Metro Ethernet terminology.
Table 8-1 VLAN-Transparent Service Versus VLAN-Specific Services
VLAN-Transparent Services VLAN-Specific Services
Bridging only Bridging or routing
One service per port Up to 254 VLAN-specific services per port
Applies indiscriminately to all VLANs on the
physical interface
Applies only to specified VLANs