6-11
Cisco ONS 15310-CL and Cisco ONS 15310-MA Ethernet Card Software Feature and Configuration Guide R8.5
78-18133-01
Chapter 6 Configuring STP and RSTP on the ML-Series Card
RSTP Features
Rapid Convergence
The RSTP provides for rapid recovery of connectivity following the failure of switch, a switch port, or
a LAN. It provides rapid convergence for new root ports, and ports connected through point-to-point
links as follows:
• Root ports—If the RSTP selects a new root port, it blocks the old root port and immediately
transitions the new root port to the forwarding state.
• Point-to-point links—If you connect a port to another port through a point-to-point link and the local
port becomes a designated port, it negotiates a rapid transition with the other port by using the
proposal-agreement handshake to ensure a loop-free topology.
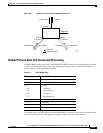
As shown in Figure 6-4, Switch A is connected to Switch B through a point-to-point link, and all of the
ports are in the blocking state. Assume that the priority of Switch A is a smaller numerical value than
the priority of Switch B. Switch A sends a proposal message (a configuration BPDU with the proposal
flag set) to Switch B, proposing itself as the designated switch.
After receiving the proposal message, Switch B selects as its new root port the port from which the
proposal message was received, forces all non-edge ports to the blocking state, and sends an agreement
message (a BPDU with the agreement flag set) through its new root port.
After receiving an agreement message from Switch B, Switch A also immediately transitions its
designated port to the forwarding state. No loops in the network are formed because Switch B blocked
all of its non-edge ports and because there is a point-to-point link between Switches A and B.
When Switch C is connected to Switch B, a similar set of handshaking messages are exchanged. Switch
C selects the port connected to Switch B as its root port, and both ends immediately transition to the
forwarding state. With each iteration of this handshaking process, one more switch joins the active
topology. As the network converges, this proposal-agreement handshaking progresses from the root
toward the leaves of the spanning tree.
The switch determines the link type from the port duplex mode: a full-duplex port is considered to have
a point-to-point connection; a half-duplex port is considered to have a shared connection.