10-21
User Guide for Cisco Secure ACS for Windows Server
78-16592-01
Chapter 10 System Configuration: Authentication and Certificates
About Certification and EAP Protocols
Master Key and PAC TTLs
The TTL values for master keys and PACs determine their states, as described in
About Master Keys, page 10-15 and About PACs, page 10-17. Master key and
PAC states determine whether someone requesting network access with
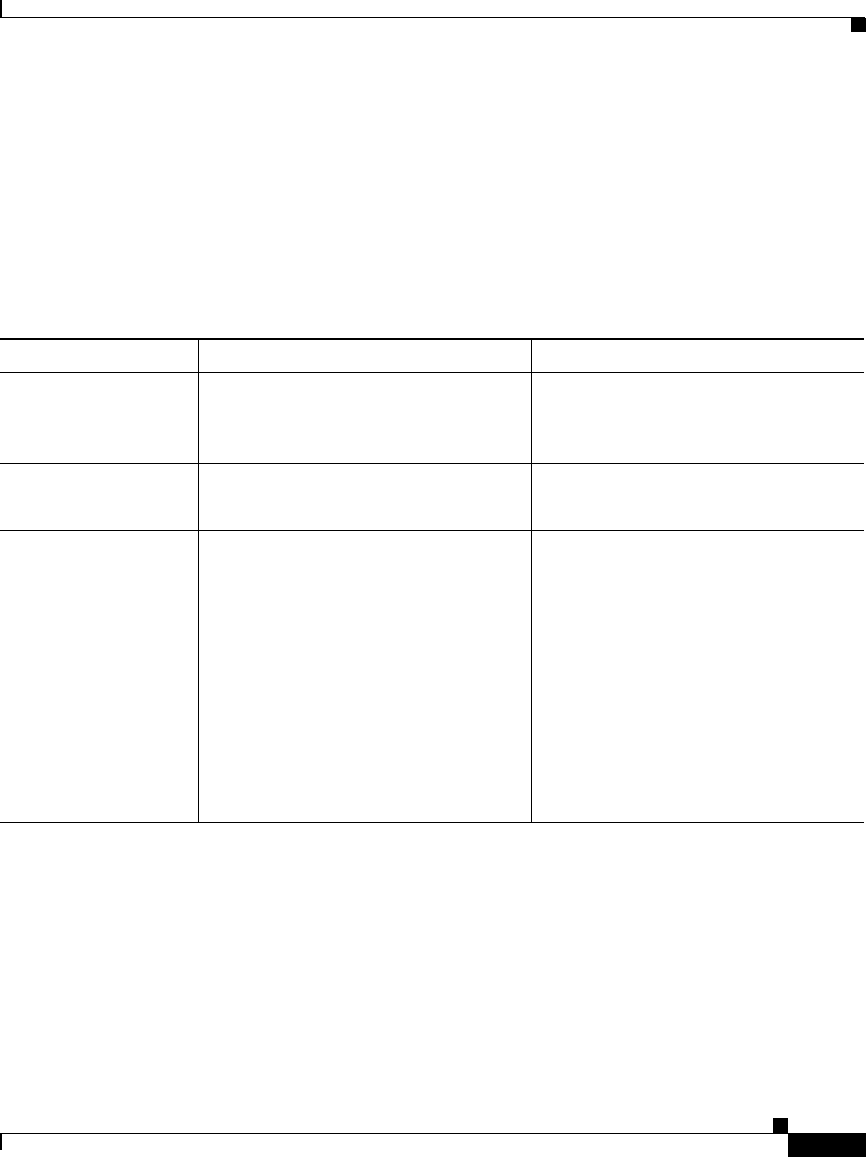
EAP-FAST requires PAC provisioning or PAC refreshing. Table 10-1 summarizes
Cisco Secure ACS behavior with respect to PAC and master key states.
Table 10-1 Master Key versus PAC States
Master key state PAC active PAC expired
Master key active Phase one succeeds.
PAC is not refreshed at end of phase
two.
Phase one succeeds.
PAC is refreshed at end of phase two.
Master key retired Phase one succeeds.
PAC is refreshed at end of phase two.
Phase one succeeds.
PAC is refreshed at end of phase two.
Master key expired PAC provisioning is required.
If automatic provisioning is enabled,
phase zero occurs and a new PAC is
sent. The end-user client initiates a
new EAP-FAST authentication
request using the new PAC.
If automatic provisioning is disabled,
phase zero does not occur and phase
one fails. You must use manual
provisioning to give the user a new
PAC.
PAC provisioning is required.
If automatic provisioning is enabled,
phase zero occurs and a new PAC is
sent. The end-user client initiates a
new EAP-FAST authentication
request using the new PAC.
If automatic provisioning is disabled,
phase zero does not occur and phase
one fails. You must use manual
provisioning to give the user a new
PAC.


















