xStack
®
DES-3200-10/18/28/28F Layer 2 Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
Appendix A
Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attacks Using Packet
Content ACL
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is the standard method for finding a host's hardware address (MAC address)
when only its IP address is known. This protocol is vulnerable because it can spoof the IP and MAC information in the
ARP packets to attack a LAN (known as ARP spoofing). This document is intended to introduce ARP protocol, ARP
spoofing attacks, and the counter measure brought by D-Link's switches to counter the ARP spoofing attack.
• How Address Resolution Protocol works
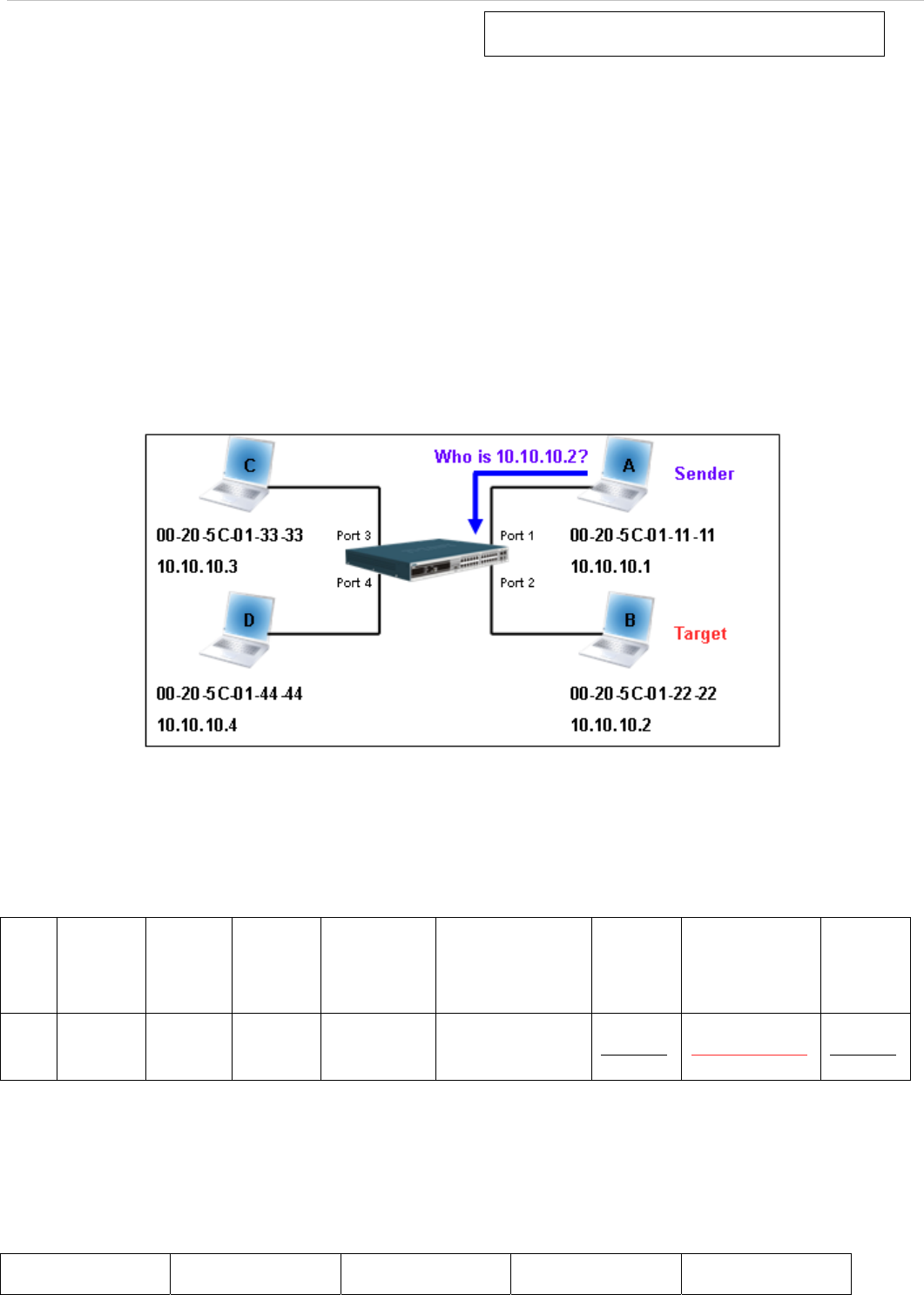
In the process of ARP, PC A will, firstly, issue an ARP request to query PC B’s MAC address. The network structure is
shown in Figure-1.
Figure-1
In the mean time, PC A’s MAC address will be written into the “Sender H/W Address” and its IP address will be written
into the “Sender Protocol Address” in ARP payload. As PC B’s MAC address is unknown, the “Target H/W Address”
will be “00-00-00-00-00-00” while PC B’s IP address will be written into the “Target Protocol Address”, shown in Table-
1.
H/W
type
Protocol
type
H/W
address
length
Protocol
address
length
Operation Sender
H/W address
Sender
protocol
address
Target
H/W address
Target
protocol
address
ARP
request
00-20-5C-01-11-11
10.10.10.1 00-00-00-00-00-00 10.10.10.2
Table -1 (ARP Payload)
The ARP request will be encapsulated into Ethernet frame and sent out. As can be seen in Table-2, the “Source
Address” in the Ethernet frame will be PC A’s MAC address. Since an ARP request is sent via a broadcast, the
“Destination address” is in the format of an Ethernet broadcast (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF).
Destination Source address Ether-type ARP FCS
218