xStack
®
DES-3200-10/18/28/28F Layer 2 Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
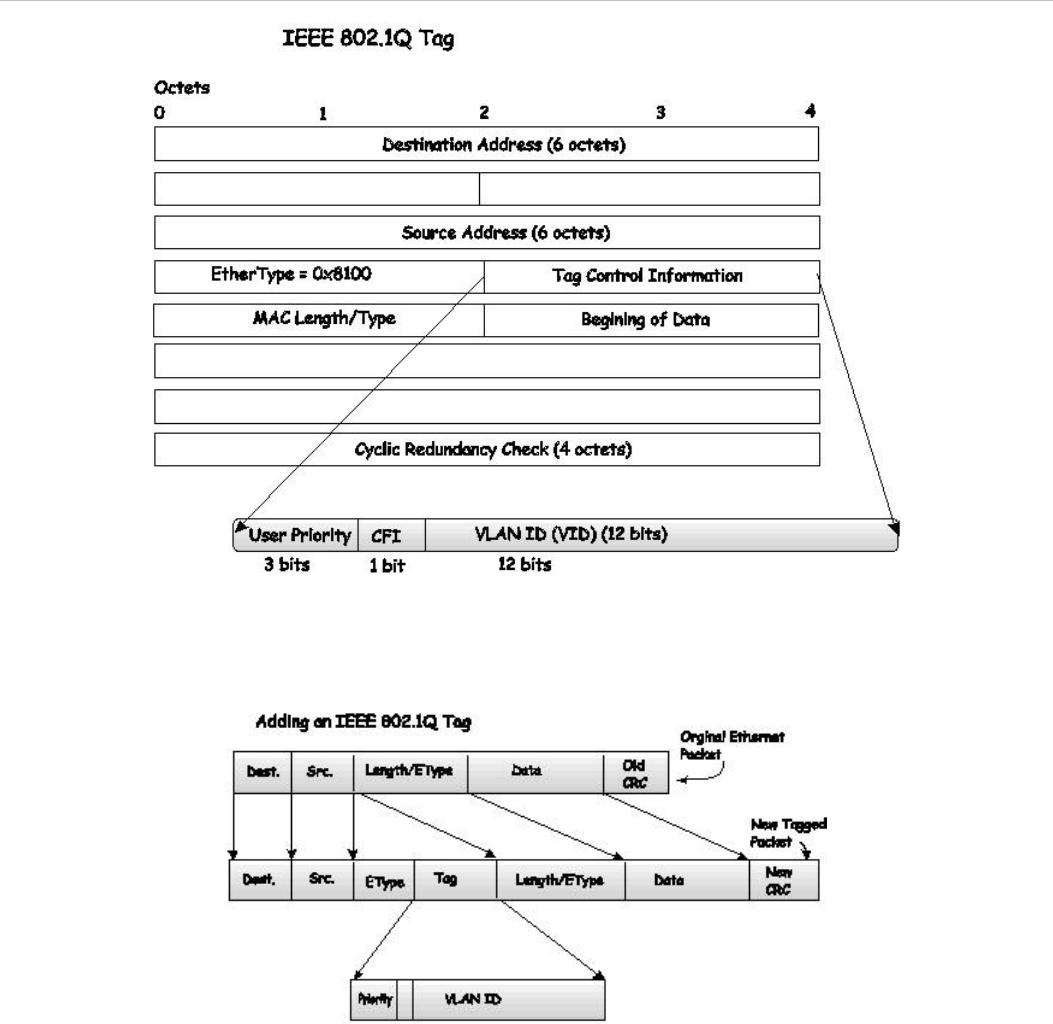
Figure 3 - 3. IEEE 802.1Q Tag
The EtherType and VLAN ID are inserted after the MAC source address, but before the original EtherType/Length or
Logical Link Control. Because the packet is now a bit longer than it was originally, the Cyclic Redundancy Check
(CRC) must be recalculated.
Figure 3 - 4. Adding an IEEE 802.1Q Tag
Port VLAN ID
Packets that are tagged (are carrying the 802.1Q VID information) can be transmitted from one 802.1Q compliant
network device to another with the VLAN information intact. This allows 802.1Q VLANs to span network devices (and
indeed, the entire network, if all network devices are 802.1Q compliant).
Unfortunately, not all network devices are 802.1Q compliant. These devices are referred to as tag-unaware. 802.1Q
devices are referred to as tag-aware.
Prior to the adoption of 802.1Q VLANs, port-based and MAC-based VLANs were in common use. These VLANs relied
upon a Port VLAN ID (PVID) to forward packets. A packet received on a given port would be assigned that port's PVID
and then be forwarded to the port that corresponded to the packet's destination address (found in the Switch's
forwarding table). If the PVID of the port that received the packet is different from the PVID of the port that is to
transmit the packet, the Switch will drop the packet.
Within the Switch, different PVIDs mean different VLANs (remember that two VLANs cannot communicate without an
external router). So, VLAN identification based upon the PVIDs cannot create VLANs that extend outside a given
switch (or switch stack).
60


















