Advanced Topics: Virtual Private Networking Page 53
Virtual Private Networking
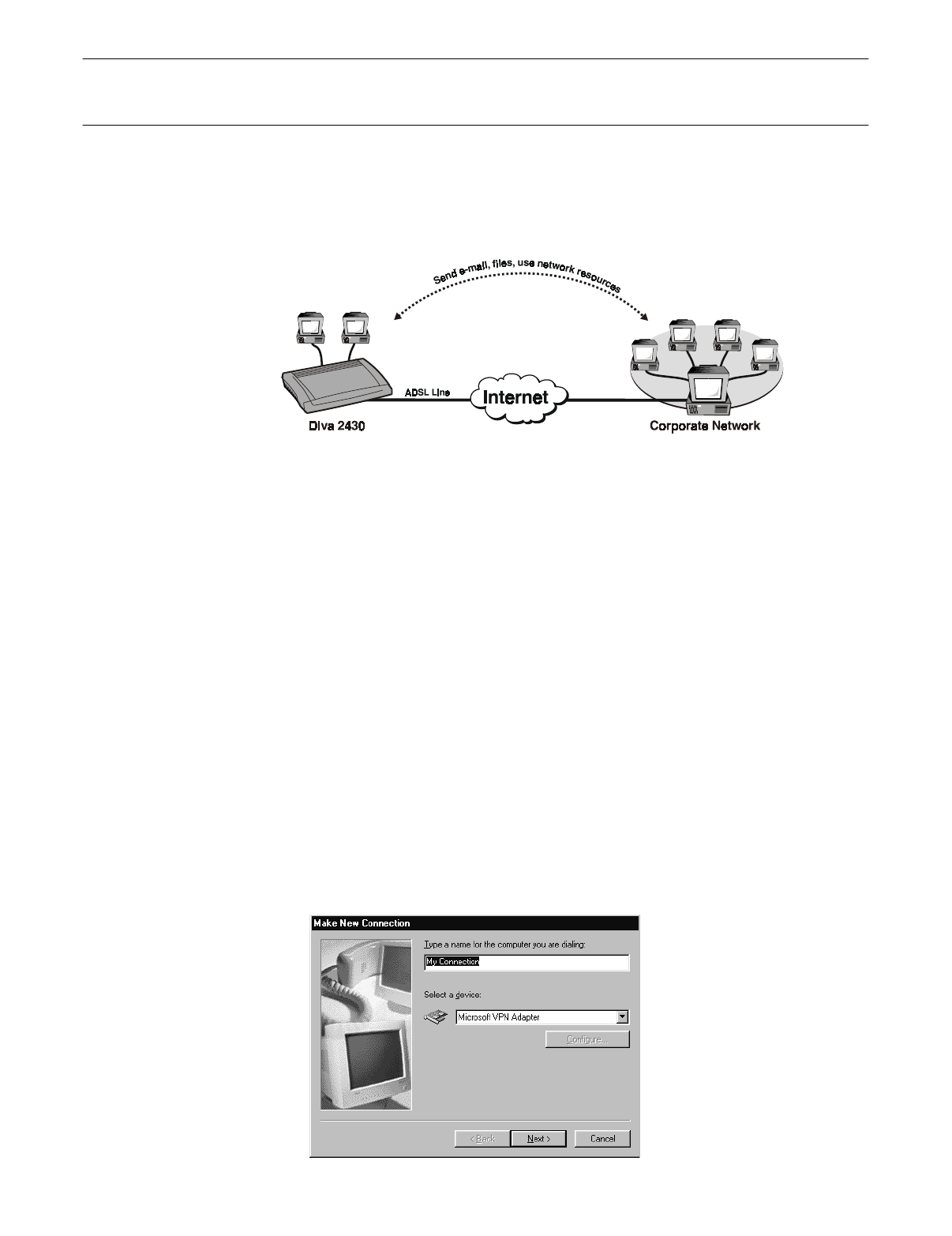
A virtual private network (VPN) is an interconnection between two networks that uses
the PPTP (point-to-point tunneling protocol). By using the Internet to transport data, a
VPN can eliminate long distance charges associated with traditional dial-up solutions.
Since PPTP provides a secure connection, network security is not compromised.
If you are using Windows 95, Dial-Up Networking 1.3 (available from Microsoft’s
web site at http://www.microsoft.com) is required to create a VPN. Do not install
DUN 1.3 on Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, or Windows Me, as a
VPN adapter is included with these operating systems; however, it may not be
installed (see below).
Before you Begin
Before you begin creating the VPN:
1.
Make sure your Internet access is working properly.
2.
Contact the administrator of the network you want to attach to and obtain the
following:
• the IP address or host name of the VPN server
• A user name and password for each user that will be connected to the VPN
Setting up a VPN with Windows 95 or Windows 98
1.
Create a new connection. To do this, double-click ‘My Computer’, double-click
‘Dial-Up Networking’, then double-click ‘Make New Connection’. You will see
the following dialog box.


















