HARSFEN0602
adapt to the specific amplifier model you bought.
Units".
Program PL[1] smaller then MC if you don't want to utilize the full power of the amplifier –
because the amplifier is oversized with respect to the application, or because the line voltage
is not enough to drive MC amperes into the motor. Do not specify
M
B
R
V
]1[PL > , where
B
V is the DC motor supply voltage and where
M
R is the motor resistance. We advise to
choose PL[1] small enough so that at peak current there is enough voltage to drive current
changes. Otherwise, at large currents the amplifier speed of response will be limited by
voltage saturation.
The continuous current limit for your application is programmed by CL[1]. The parameter
CL[1] cannot exceed MC/2, since greater continuous currents will risk amplifier
overheating.
You may set CL[1] < MC/2 to avoid motor overheating.
We advice to select PL[1] and CL[1] as large as the amplifier and the application permit.
This will extend the linear range of the amplifier to maximum and will thus optimize the
servo performance.
The decision if to limit the motor current demand to CL[1] or to PL[1] is made by the
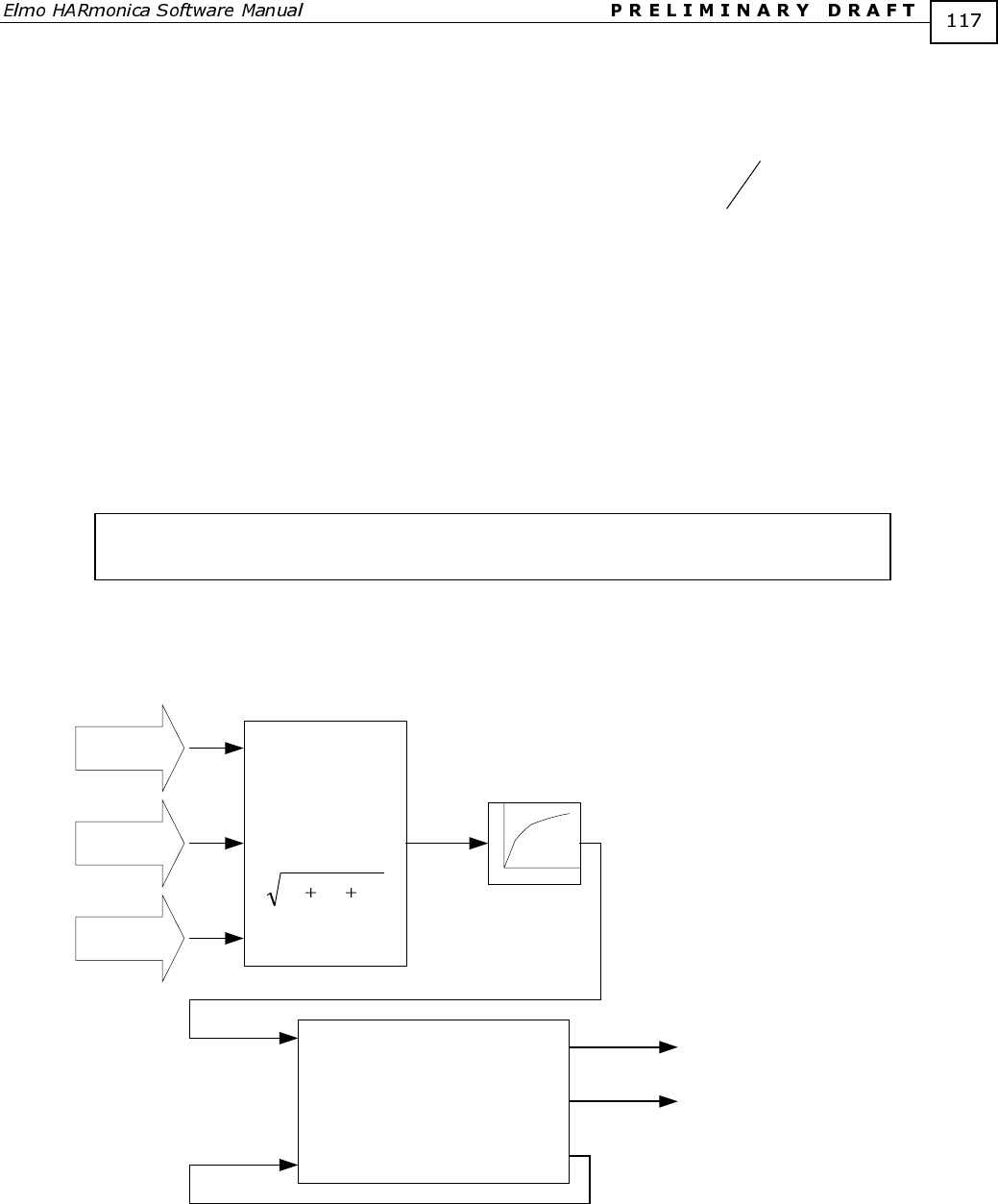
amplifier in real-time. The LC flag reports the current limiting status. The decision
mechanism is depicted below.
-
Ic
Ib
Ia
RMS
2
c
2
b
2
a
III
If RMS > THOLD, then
LIMIT=CL[1]
THOLD=0.9CL[1]
LC=1
else
LIMIT=PL[1]
THOLD=CL[1]
LC=0
THOLD
LIMIT (CL[1] or PL[1])
RMS
Low Pass filter
Filtered RMS current
LC
Figure 11: Peak/Continuous current limit selection
When the current limit switches, the comparison threshold (named THOLD in the figure
above) is slightly changed. This hysteresis prevents to frequent switching of the current
limit.
Slower time constants in the low pass filter will permit a peak current demand for longer
times, but will also take more time to recover from a limiting to CL[1]. The time constant
τ of the low pass filter is selected by PL[2] as follows:
The parameters PL[1] and CL[1] specify limits for the current demand. At transients, the
motor current may exceed PL[1] and CL[1] due to overshooting.


















