NetWin 110 HBA User’s Guide Page 1-12
3. Click Disable or Enable as appropriate.
See chapter 2, BIOS Utility Configuration Guide, for information on enabling the BIOS on an HBA and configuring
the BIOS utility.
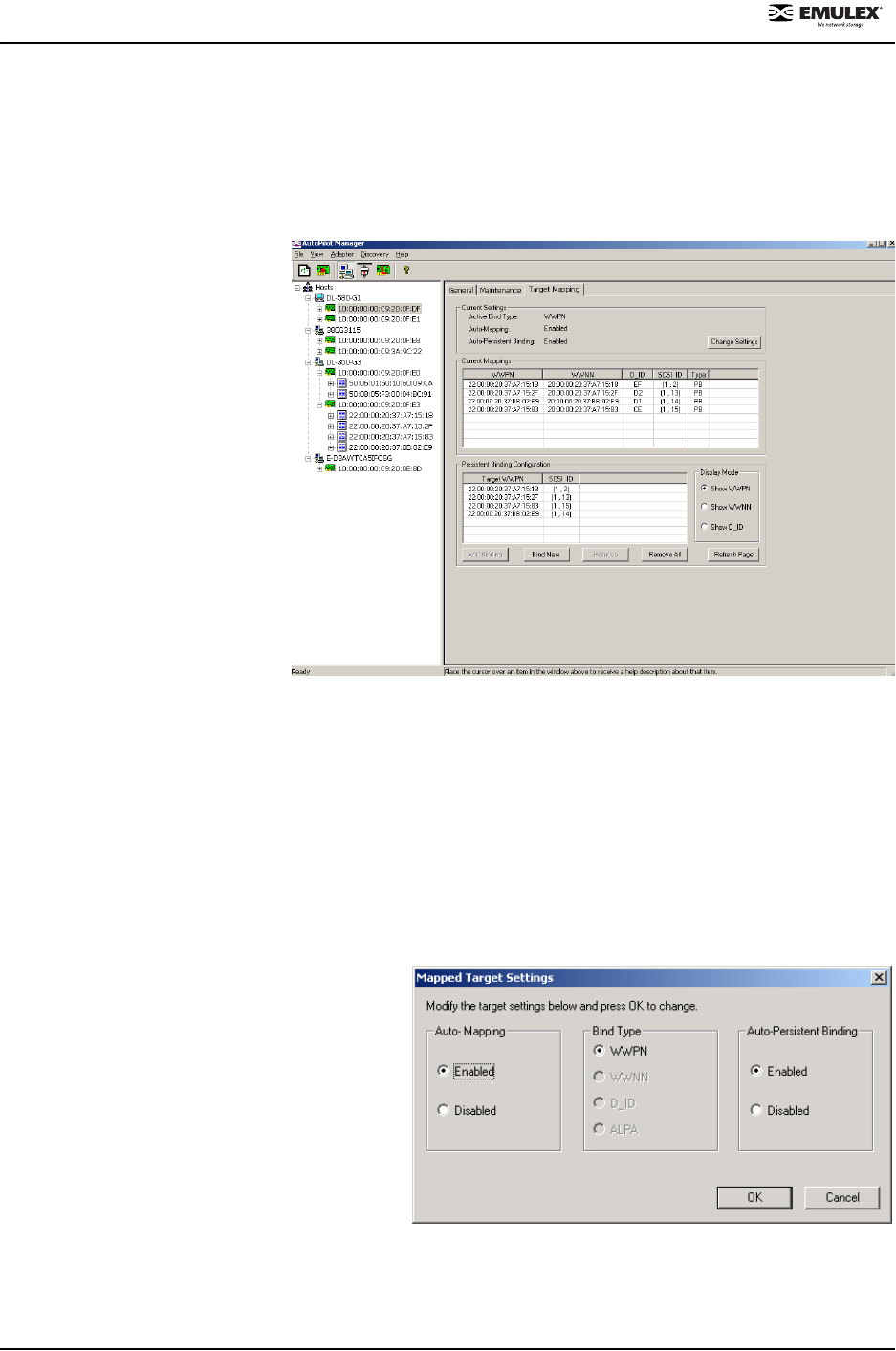
1.5.2. Mapping Targets and Editing Persistent Bindings
The Target Mapping tab enables you
to modify the mapped target settings
and to create, add, edit and remove
persistent bindings.
Note: You must select
Advanced Mode from
the View menu to see
the Maintenance and
Target Mapping tabs
associated with a
selected HBA.
Auto-Persistent Binding
The Auto-Persistent Binding server
is normally running when the host is
running. Its purpose is to
persistently bind any new targets
that are added to the SAN with the
auto-mapped values.
Note: Before you modify the persistent bindings of an adapter on a local or remote host, you must
disable the Auto-Persistent Binding server first. This prevents the Auto-Persistent Binding server
from interfering with the changes you make to the persistent bindings.
Changing Current Settings
The Current Settings area of the Target Mapping tab displays the Active Bind Type in use and whether or not
Automapping is enabled.
To change current settings, do the following:
1. In the discovery tree, select the HBA whose current settings you wish to change.
2. Click the Target Mapping tab and click
Change Settings. The Mapped Target
Settings dialog box appears.
3. Modify the target settings as desired and
click OK.
Current Mappings
Current mappings are displayed by World Wide
Port Name (WWPN), World Wide Node Name
(WWNN), device ID (D_ID), SCSI ID, or Type.
Type can be either 'PB', indicating that the mapping
was the result of a persistent binding, or 'Auto',
indicating that the target was automapped.
