Using Memory
Your computer can use up to 8MB of memory. This section
describes how the memory in your computer works. Also be
sure to see your operating system manual for complete
information on memory management.
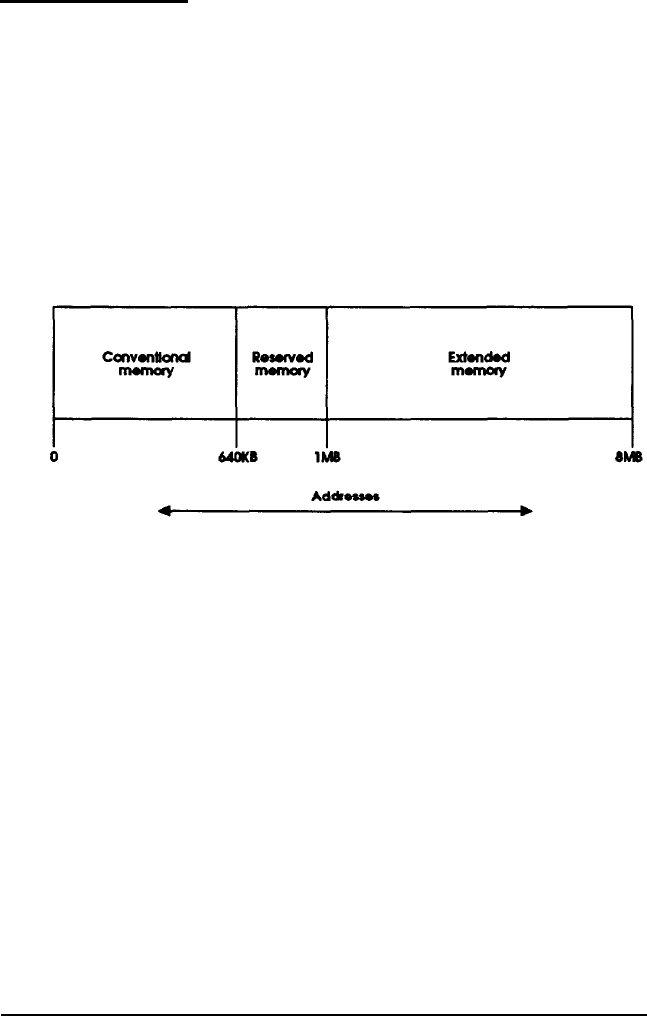
A computer’s memory is divided into three types:
conventional, reserved, and extended. The following diagram
shows the relationships between these types of memory and
their addresses.
All memory in a computer is managed using addresses—
numbers that describe the location of each byte of data. Each
memory chip must have its own set of unique addresses so that
the operating system knows where to store and find data.
Conventional memory is memory that MS-DOS recognizes and
manages directly. The size of conventional memory is limited
to 640KB and has addresses in the range 0 to 640KB.
Reserved memory is memory in the range 640KB to 1MB. The
system enhances its performance by using 128KB of this
memory as shadow RAM, and the remaining memory is
available.
3-22
Using Your Computer