Configuring for Network Management Applications
CDP
4. If a CDP switch does not detect an IP address on the connecting port of
a CDP neighbor, then the loopback IP address is used (127.0.0.1).
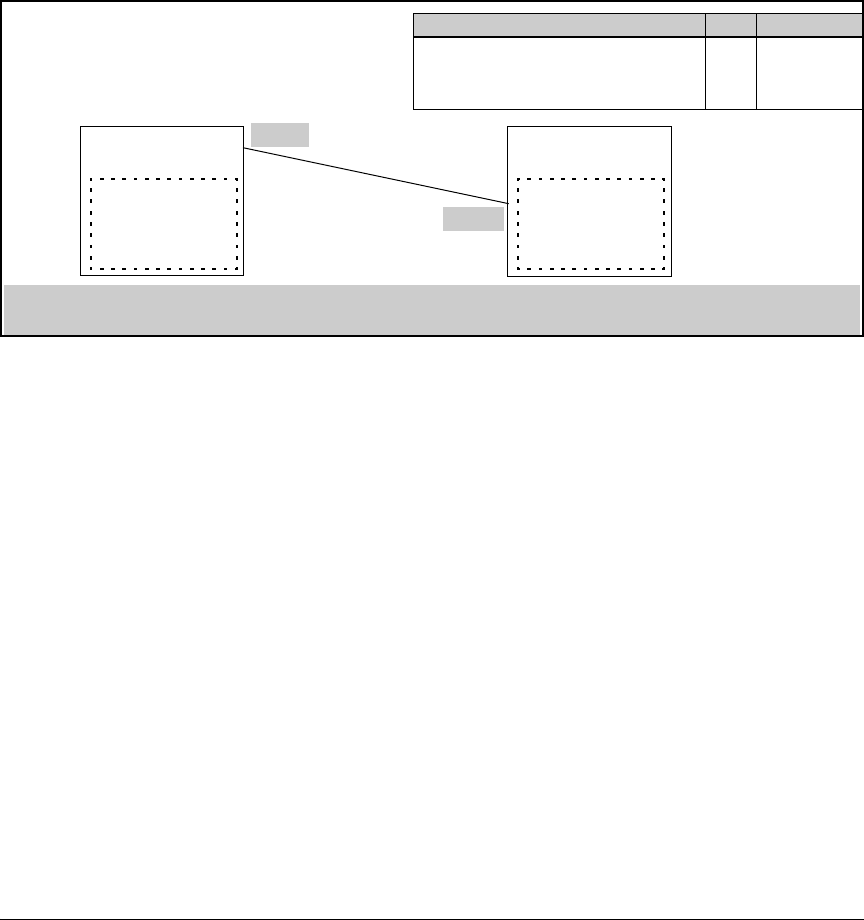
For example, in figure 13-20, port A1 on CDP switch “X” is connected to port
C5 on CDP neighbor switch “Y”, with the indicated VLAN configuration on
port C5:
Switch "X"
CDP Enabled on Port A1
CDP Neighbor Table
Port | Data
------|------------------
A1 | 10.28.227.103
Switch "Y"
CDP Enabled on Port C5
CDP Neighbor Table
Port | Data
------|------------------
C5 | Switch "X" data
Port A1
Port C5
VLAN Membership in Port C5 of Switch "Y" VID IP Address?
DEFAULT_VLAN (Primary VLAN) 1 No
Blue_VLAN 200 10.28.227.103
Red VLAN 300 10.28.227.88
Thus, CDP switch "X" detects CDP switch "Y" on port A1 and shows 10.28.227.103 in its CDP table entry because in CDP switch "Y" the
Primary VLAN does not have an IP address and the Blue_VLAN has a lower VID than the Red_VLAN.
Figure 13-20. Example of IP Address Selection when a CDP Neighbor Has Multiple VLANs with IP
Addresses
CDP Neighbor Data and MIB Objects
The switch places the data received from inbound CDP packets into its MIB
(Management Information Base). This data is available in three ways:
■ Using the switch’s show cdp neighbors command to display a subset of
Neighbor data
■ Using the walkmib command to display a listing of the CDP MIB objects
■ Electronically, using an SNMP utility designed to search the MIB for
CDP data
As shown under “Viewing the Switch’s Current CDP Neighbors Table” on page
13-32, you can list a subset of data for each CDP device currently found in the
switch’s CDP Neighbors table. Table 13-4, “CDP Neighbors Data”, describes
the CDP Neighbor data set available in the switch.
13-38


















