QinQ (Provider Bridging)
Introduction
How QinQ Works
Under QinQ, the provider network operates on a different VLAN space,
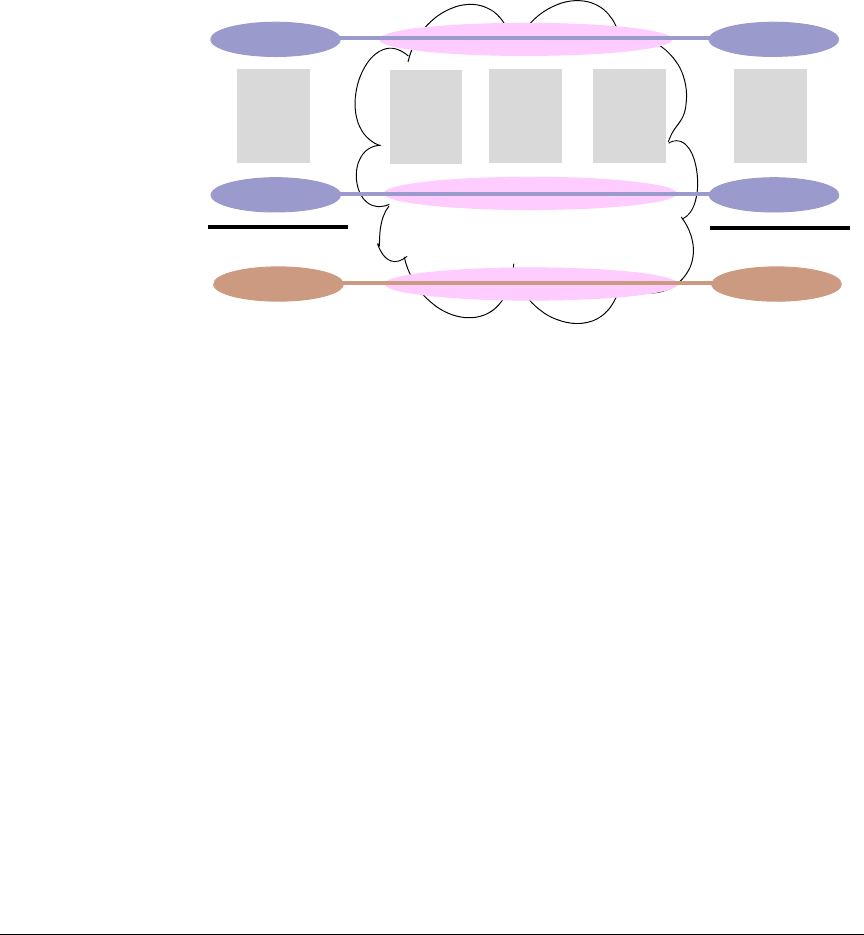
independent of the VLANs that are used in the customer network as shown in
Figure 8-2.
Service Provider Network
Provider
Edge
C-VLAN
Bridge
C-VLAN
Bridge
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
VLAN 1
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
VLAN 1
Service VLAN 100
Bridge
Provider
Edge
Bridge
Service VLAN 101
Service VLAN 102
Customer A
Customer A
Customer B
Customer B
Provider
Core
Bridge
Figure 8-2. Example of VLANs in a QinQ Configuration
Customer VLANs (referred to as C-VLANs by the IEEE 802.1ad specification)
are not used to make any forwarding decisions inside the provider network
where customer frames get assigned to service VLANs (S-VLANs). Inside the
provider cloud, frames are forwarded based on the S-VLAN tag only, while the
C-VLAN tag remains shielded during data transmission. The S-VLAN tag is
removed when the frame exits the provider network, restoring the original
customer frame.
Features and Benefits
■ Increases the VLAN space in a provider network or enterprise backbone.
■ Reduces the number of VLANs that a provider needs to support within the
provider network for the same number of customers.
■ Enables customers to plan their own VLAN IDs, without running into
conflicts with service provider VLAN IDs.
■ Provides a simple Layer 2 VPN solution for small-sized MANs (Metropol-
itan Area Networks) or intranets.
■ Provides for customer traffic isolation at Layer 2 within a Service Provider
network.
8-5


















