58 Chapter 1
SNA Terms and Concepts
Basic APPN Concepts
data. In ISR, once a session route has been established, all data on
that session uses the same route. If part of the route fails, the session
ends.
• In automatic network routing (ANR), available in network nodes that
support APPN's High-Performance Routing (HPR) function,
intermediate network nodes can dynamically reroute session traffic if
part of the route fails. ANR does not provide intermediate session
pacing or segmentation and reassembly.
ANR enables intermediate nodes to route session traffic much faster
than is possible with traditional APPN ISR. However, ANR requires
additional overhead at the RTP (Rapid Transport Protocol) endpoints. In
routes with few intermediate nodes, an ANR route might actually be
slower than an ISR route, due to processing time at the endpoints. For
routes containing a larger number of intermediate nodes (hops), ANR
routes are typically faster. The exact location of the break-even point
depends on the efficiency of the RTP nodes.
Direct Connectivity
Direct connectivity enables session traffic to travel directly between two
nodes without the need for an APPN network node to route the session.
In general, sessions between directly connected nodes can exchange data
more quickly than sessions for which data is routed through a network
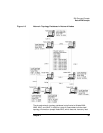
node. For nodes on a shared-access transport facility (SATF)—for
example, for nodes on a token ring as shown in Figure 1-9—efficiency
would be increased by defining links between every pair of nodes in your
network. However, this can be a difficult task—the number of link
stations is n × (n−1), where n is the number of nodes in the network.
An APPN network on a token ring is shown in Figure 1-9, “APPN
Network Using a Shared-Access Transport Facility.”