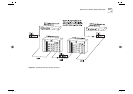
What is LAN Emulation (LANE)? 2-5
Joining the ELAN
Before a LAN Emulation Client (LEC) can transmit any
Ethernet frames onto the ATM network it must first
join an ELAN. To join the ELAN:
1
The LEC must know the name of the ELAN it is to
join.
The ELAN name is specified through the management
software on the Switch.
2
The LEC must communicate with the LAN
Emulation Server (LES) that is serving that ELAN.
To communicate with the LES, the LEC must first
locate the LES. The LEC can find the ATM address of
the LES in one of the following ways:
■
If there is a LAN Emulation Configuration Server
(LECS) on the network, the LEC gets the address of
the LES from the LECS.
The way in which the LECS determines which LES
the LEC needs to communicate with, depends on
the
policy
that the LECS is running. Refer to the
user guide that accompanies your LECS for more
details of the policies your LECS uses.
■
If the network does not have a LECS, the LEC gets
the LES address from the management software
on the ATM device.
3
The LEC must have a connection to the
Broadcast and Unknown Server (BUS).
When the LEC has joined the LES, the LES helps the
LEC locate the
Broadcast and Unknown Server
(BUS)
associated with that ELAN.
Locating the LECS
Before the LEC can ask the LECS for the address of
the LES, the LEC must first locate the LECS. There are
three ways in which the LEC can locate the LECS, and
the LEC tries these methods in the following order:
■
The LEC can ask the adjacent ATM Switch using
the
Interim Local Management Interface (ILMI)
.
■
The LEC can use a well known ATM address that is
reserved for the LECS. The well known address is
pre-programmed into most LECS devices. The well
known address is:
47007900000000000000000000:00A03E000001:00
■
The LEC can use a reserved
Permanent Virtual
Circuit (PVC)
which the ATM Switch has already
routed to the LECS. The reserved PVC is
VPI 0, VCI 17.