Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5400 Series TMDG 19
Thermal/Mechanical Reference Design
A potential mechanical solution for heavy heatsinks is the direct attachment of the
heatsink to the chassis pan. In this case, the strength of the chassis pan can be utilized
rather than solely relying on the baseboard strength. In addition to the general
guidelines given above, contact with the baseboard surfaces should be minimized
during installation in order to avoid any damage to the baseboard.
The Intel reference design for Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5400 Series is using
such a heatsink attachment scheme. Refer to Section 2.5 for further information
regarding the Intel reference mechanical solution.
2.2 Processor Thermal Parameters and Features
2.2.1 Thermal Control Circuit and TDP
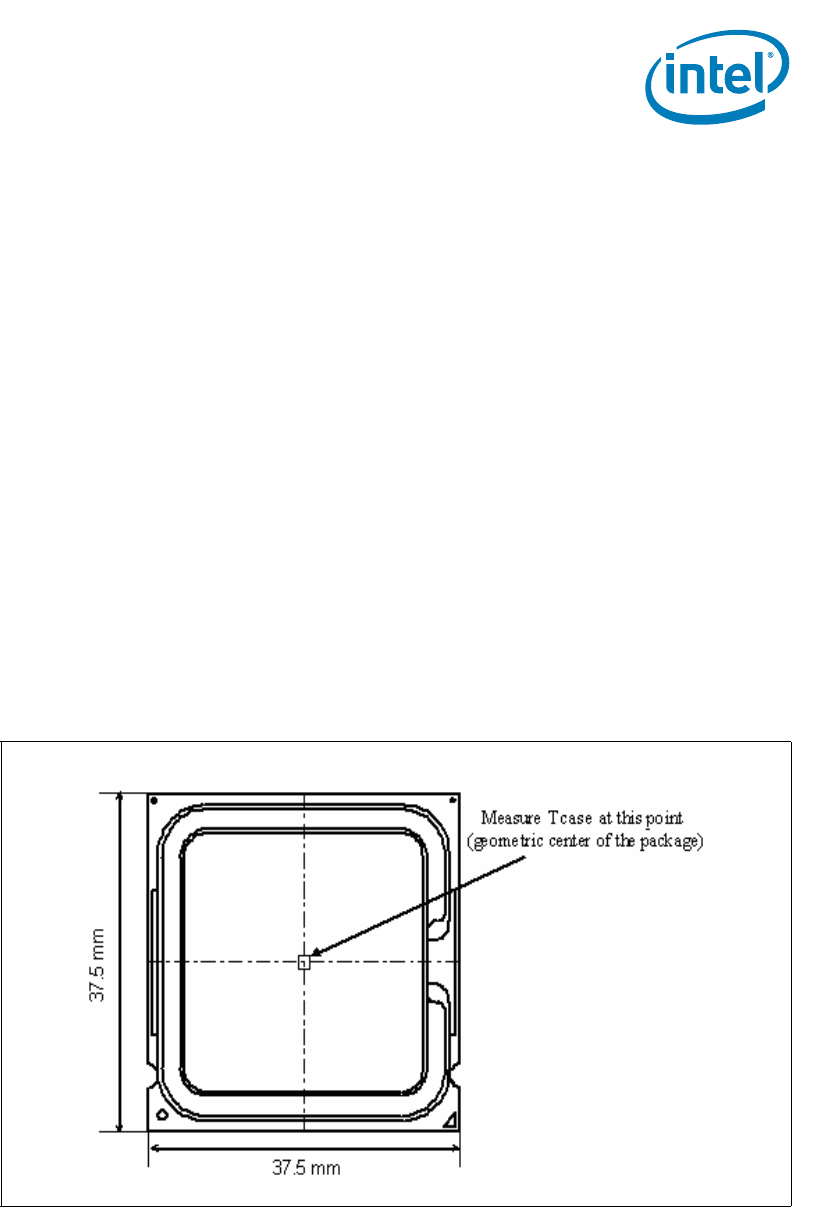
The operating thermal limits of the processor are defined by the Thermal Profile. The
intent of the Thermal Profile specification is to support acoustic noise reduction through
fan speed control and ensure the long-term reliability of the processor. This
specification requires that the temperature at the center of the processor IHS, known
as (T
CASE
) remains within a certain temperature specification. For illustration,
Figure 2-4 shows the measurement location for the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5400 Series package. Compliance with the T
CASE
specification is required to
achieve optimal operation and long-term reliability (See the Intel
®
Xeon
®
Dual- and
Multi- Processor Family Thermal Test Vehicle User's Guide for Case Temperature
definition and measurement methods).
To ease the burden on thermal solutions, the Thermal Monitor feature and associated
logic have been integrated into the silicon of the processor. One feature of the Thermal
Monitor is the Thermal Control Circuit (TCC). When active, the TCC lowers the
processor temperature by reducing power consumption. This is accomplished through a
combination of Thermal Monitor and Advanced Thermal Monitor (TM2). Thermal
Monitor modulates the duty cycle of the internal processor clocks, resulting in a lower
effective frequency. When active, the TCC turns the processor clocks off and then back
on with a predetermined duty cycle. Thermal Monitor 2 activation adjusts both the
Figure 2-4. Processor Case Temperature Measurement Location