Datasheet, Volume 1 71
Signal Description
6.9 Error and Thermal Protection Signals
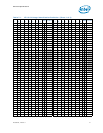
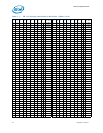
Table 6-11. Error and Thermal Protection Signals
Signal Name Description
Direction/
Buffer Type
CATERR#
Catastrophic Error: This signal indicates that the system has
experienced a catastrophic error and cannot continue to operate.
The processor will set this for non-recoverable machine check
errors or other unrecoverable internal errors.
On the processor, CATERR# is used for signaling the following
types of errors:
• Legacy MCERRs – CATERR# is asserted for 16 BCLKs.
• Legacy IERRs – CATERR# remains asserted until warm or
cold reset.
O
CMOS
PECI
PECI (Platform Environment Control Interface): A serial
sideband interface to the processor, it is used primarily for
thermal, power, and error management.
I/O
Asynchronous
PROCHOT#
Processor Hot: PROCHOT# goes active when the processor
temperature monitoring sensor(s) detects that the processor has
reached its maximum safe operating temperature. This indicates
that the processor Thermal Control Circuit (TCC) has been
activated, if enabled. This signal can also be driven to the
processor to activate the TCC.
Note: Toggling PROCHOT# more than once in 1.5 ms period
will result in constant Pn state of the processor.
CMOS Input/
Open-Drain
Output
THERMTRIP#
Thermal Trip: The processor protects itself from catastrophic
overheating by use of an internal thermal sensor. This sensor is
set well above the normal operating temperature to ensure that
there are no false trips. The processor will stop all execution
when the junction temperature exceeds approximately 130 °C.
This is signaled to the system by the THERMTRIP# signal.
O
Asynchronous
CMOS