Configuring the Switch
3-130
3
Command Attributes
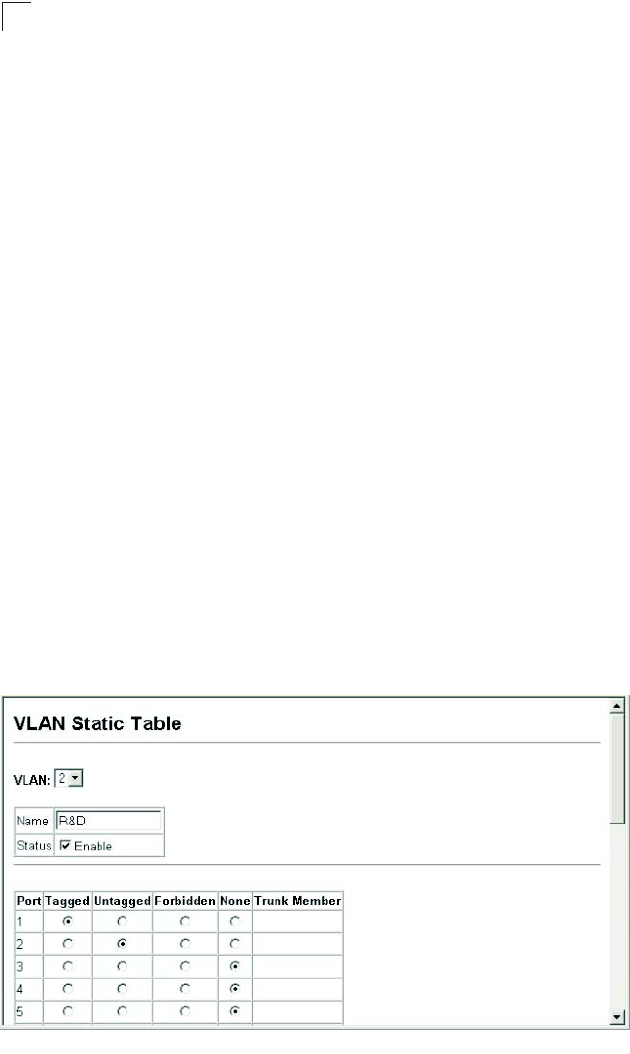
• VLAN – ID of configured VLAN (1-4094, no leading zeroes).
• Name – Name of the VLAN (1 to 32 characters).
• Status – Enables or disables the specified VLAN.
- Enable: VLAN is operational.
- Disable: VLAN is suspended; i.e., does not pass packets.
• Port – Port identifier.
• Trunk – Trunk identifier.
• Membership Type – Select VLAN membership for each interface by marking the
appropriate radio button for a port or trunk:
- Tagged: Interface is a member of the VLAN. All packets transmitted by the port
will be tagged, that is, carry a tag and therefore carry VLAN or CoS information.
- Untagged: Interface is a member of the VLAN. All packets transmitted by the
port will be untagged, that is, not carry a tag and therefore not carry VLAN or
CoS information. Note that an interface must be assigned to at least one group
as an untagged port.
- Forbidden: Interface is forbidden from automatically joining the VLAN via
GVRP. For more information, see “Automatic VLAN Registration” on page
3-124.
- None: Interface is not a member of the VLAN. Packets associated with this
VLAN will not be transmitted by the interface.
• Trunk Member – Indicates if a port is a member of a trunk. To add a trunk to the
selected VLAN, use the last table on the VLAN Static Table page.
Web – Click VLAN, 802.1Q VLAN, Static Table. Select a VLAN ID from the
scroll-down list. Modify the VLAN name and status if required. Select the
membership type by marking the appropriate radio button in the list of ports or
trunks. Click Apply.
Figure 3-74 VLAN Static Table - Adding Static Members


















