NETGEAR genie ADVANCED Home
48
D6200 WiFi DSL Modem Router
• NAT Filtering. Network Address Translation (NAT) determines how the WiFi DSL
modem router processes inbound traffic. Secured NAT provides a secured firewall to
protect the computers on the LAN from attacks from the Internet, but might prevent
some Internet games, point-to-point applications, or multimedia applications from
functioning. Open NAT provides a much less secured firewall, but allows almost all
Internet applications to function.
• Disable SIP ALG. Some VoIP applications do not work well with the SIP ALG.
Selecting this check box to turn off the SIP ALG might help your VoIP devices to
create or accept a call through the router.
3. Click Apply.
Default DMZ Server
The default DMZ server feature is helpful when you are using some online games and
videoconferencing applications that are incompatible with Network Address Translation
(NAT). The WiFi DSL modem router is programmed to recognize some of these applications
and to work correctly with them, but other applications might not function well. In some cases,
one local computer can run the application correctly if that computer’s IP address is entered
as the default DMZ server.
WARNING:
DMZ servers pose a security risk. A computer designated as the
default DMZ server loses much of the protection of the firewall and
is exposed to exploits from the Internet. If compromised, the DMZ
server computer can be used to attack other computers on your
network.
Incoming traffic from the Internet is discarded by the WiFi DSL modem router unless the
traffic is a response to one of your local computers or a service that you have configured in
the Port Forwarding/Port Triggering screen. Instead of discarding this traffic, you can forward
it to one computer on your network. This computer is called the default DMZ server.
To set up a default DMZ server:
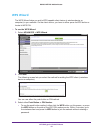
1. Select ADVANCED > Setup > WAN Setup.
2. Select the Default DMZ Server check box.
3. Type the IP address.
4. Click Apply.
Change the MTU Size
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the largest data packet a network device transmits.
When one network device communicates across the Internet with another, the data packets
travel through many devices along the way. If any device in the data path has a lower MTU