422 Configuring quality of service
NN47250-500 (Version 03.01)
QoS mode
WSS Software supports Layer 2 and Layer 3 classification and marking of traffic, to help provide end-to-end
QoS throughout the network. The following modes of QoS are supported:
• Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM)—Provides wireless QoS for time-sensitive applications such as voice and
video. WMM QoS is enabled by default and does not require any configuration.
• SpectraLink Voice Priority (SVP)—Provides optimized forwarding of SVP voice traffic. SVP QoS is
disabled by default.
Session-based Call Admission Control (CAC) is also supported. You can use CAC with either QoS mode to
ensure bandwidth availability by limiting the number of active sessions a radio can have.
The static CoS option enables you to easily set CoS for all traffic on an SSID by marking all the SSID’s traffic
with the same CoS value.
You can use ACLs to override CoS markings or set CoS for non-WMM traffic.
The following sections describe each of these options.
WMM QoS mode
WSSs and APs each provide classification and marking for WMM QoS:
• WSSs classify and mark traffic based on 802.1p tag value (for tagged traffic) or Differentiated Services
Code Point (DSCP) value.
• APs classify ingress traffic from wireless clients based on the service type value in the 802.11 header, and
mark the DSCP value in the IP tunnel on which the AP forwards the user traffic to the WSS.
APs place traffic from a WSS to a wireless client in a forwarding queue based on the DSCP
value in the tunnel carrying the traffic, then forward the traffic based on the queue’s priority.
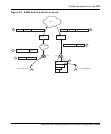
Figure 26 on page 423 shows how WSSs classify ingress traffic. Figure 27 on page 424 shows how WSSs
mark egress traffic. Figure 28 on page 425 and Figure 29 on page 426 show how APs classify ingress traffic
and mark egress traffic. The figures show the default mappings between DSCP and CoS. (For information
about changing CoS mappings, see “Changing CoS mappings” on page 435.)