Chapter 6: Technology Background
173
• Linux operating systems with the 2.6 kernel support 64-bit LBA. For these
OSes, always choose the default 512 B sector size.
See “Creating a Logical Drive” on page 65 and page 136, and “Creating a Disk
Array – Advanced Configuration” on page 132.
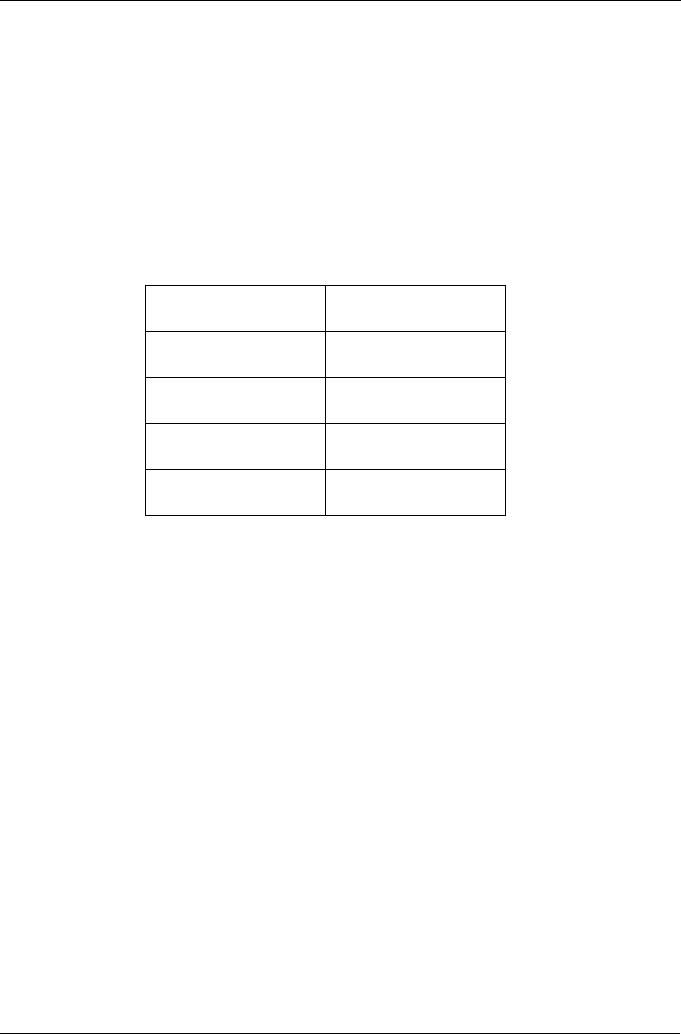
2 TB Limitation
If your Host PC runs Windows 2000 or Windows XP (32-bit), and you want to
create logical drives larger than 2 TB, you must choose a sector size larger than
512 B when you create the logical drive. The table on the next page correlates
sector size with logical drive capacity.
Also see “Ranges of Disk Array Expansion” on page 182.
Choosing Cache Policy
As it is used with SuperTrak, the term cache refers to any of several kinds of
high-speed, volatile memory that hold data moving from your computer to the
physical drives or vice-versa. Cache is important because it can read and write
data much faster than a physical drive. There are read caches, which hold data
as it is read from a physical drive; and write caches, which hold data as it is
written to a physical drive.
In order to tune the cache for best performance in different applications, user-
adjustable settings are provided. Cache settings are made in conjunction with
logical drives:
• When you create a logical drive. See “Creating a Logical Drive” on page 65
or page 136, and “Creating a Disk Array – Advanced Configuration” on
page 132.
• On an existing logical drive. See “Changing Logical Drive Settings” on
page 67 or page 145.
Logical Drive Size Sector Size
8 to 16 TB 4096 bytes (4 KB)
4 to 8 TB 2048 bytes (2 KB)
2 to 4 TB 1024 bytes (1 KB)
0 to 2 TB 512 bytes (512 B)


















