Chapter 3: Multi-Platform Client and Raritan Remote Client
123
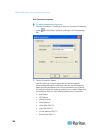
Devices can filter out the electrical interference of video output
from graphics cards. This feature optimizes picture quality and
reduces bandwidth. Higher settings transmit variant pixels only if
a large color variation exists in comparison to the neighboring
pixels. However, setting the threshold too high can result in the
unintentional filtering of desired page changes. Lower settings
transmit most pixel changes. Setting this threshold too low can
result in higher bandwidth use.
Note: The default Noise Filter is 2. Raritan recommends that you
lower this value to 0 (zero). Although higher settings will stop the
needless transmission of false color variations, true and intentional
small changes to a video image may not be transmitted.
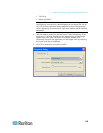
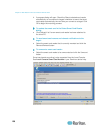
b. PLL Settings
If the video image looks extremely blurry or unfocused, the PLL
settings for clock and phase can be adjusted until a better image
appears on the active target server.
Warning: Exercise caution when changing the clock and phase
settings since doing so may result in lost or distorted video and you
may not be able to return to the previous state. Contact Raritan
Technical Support before making any changes.
Clock - Controls how quickly video pixels are displayed across
the video page. Changes made to clock settings cause the video
image to stretch or shrink horizontally. Odd number settings are
recommended. Under most circumstances this setting should not
be changed because the autodetect is usually quite accurate.
Phase - Phase values range from 0 to 31 and will wrap around.
Stop at the phase value that produces the best video image for
the active target server.
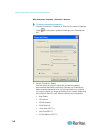
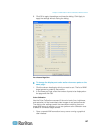
a. Color Settings -Gain control can be thought of as contrast
adjustment. Offset control can be thought of as brightness
adjustment.
Select the Link Color Controls checkbox to make all slide
adjusters move in unison when any one option is moved.
Red Gain - Controls the amplification of the red signal.
Red Offset - Controls the bias of the red signal.
Green Gain - Controls the amplification of the green signal.
Green Offset - Controls the bias of the green signal.
Blue Gain - Controls the amplification of the blue signal.
Blue Offset - Controls the bias of the blue signal.
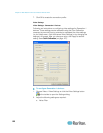
a. Color Settings - Gain control can be thought of as contrast
adjustment. Offset control can be thought of as brightness
adjustment.