13
2. Suitable and Unsuitable Objects for Scanning 3. Plane Scanning
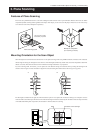
Plane scanning system
Multi-plane composition
(four scanning surfaces)
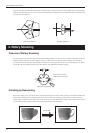
The laser light is emitted from the right side. This means that if your aim is to capture the void between the legs, for example, it is best to
mount the doll so that it faces right. The direction in which the laser light is incident is decided by the orientation of the scan object mounted
on the table. With multi-plane composition, this orientation is the first surface for scanning.
A
B
Table
Orientation of the laser light
Mounting Orientation for the Scan Object
When the object to be scanned has areas with cavities or voids, plane scanning, which uses parallel laser beams, is effective. This is because
the laser light can easily pass through the voids. However, if the laser light is blocked by another area, it becomes impossible to determine
that the void exists. This means the direction from which the laser light is beamed is very important.
If you are scanning a doll, for instance, you can capture the voids between the legs and under the arms by aiming the laser light in the
direction shown in figure A. If the orientation in figure B is used, the laser light is blocked and so the two legs end up joined.
3. Plane Scanning
Features of Plane Scanning
This mode uses parallel laser beams to scan while rotating the table and laser head in synchronization. Because this mode can obtain
comparatively stable scanning results regardless of the shape of the object, you can use it as an all-purpose mode. You can use it to scan up
to six surfaces at one time (multi-plane composition).
The laser beams strike
substantially in parallel
.