Chapter 1 Introduction Series 24-HP Instruction Manual
1-4 IM-24-HP
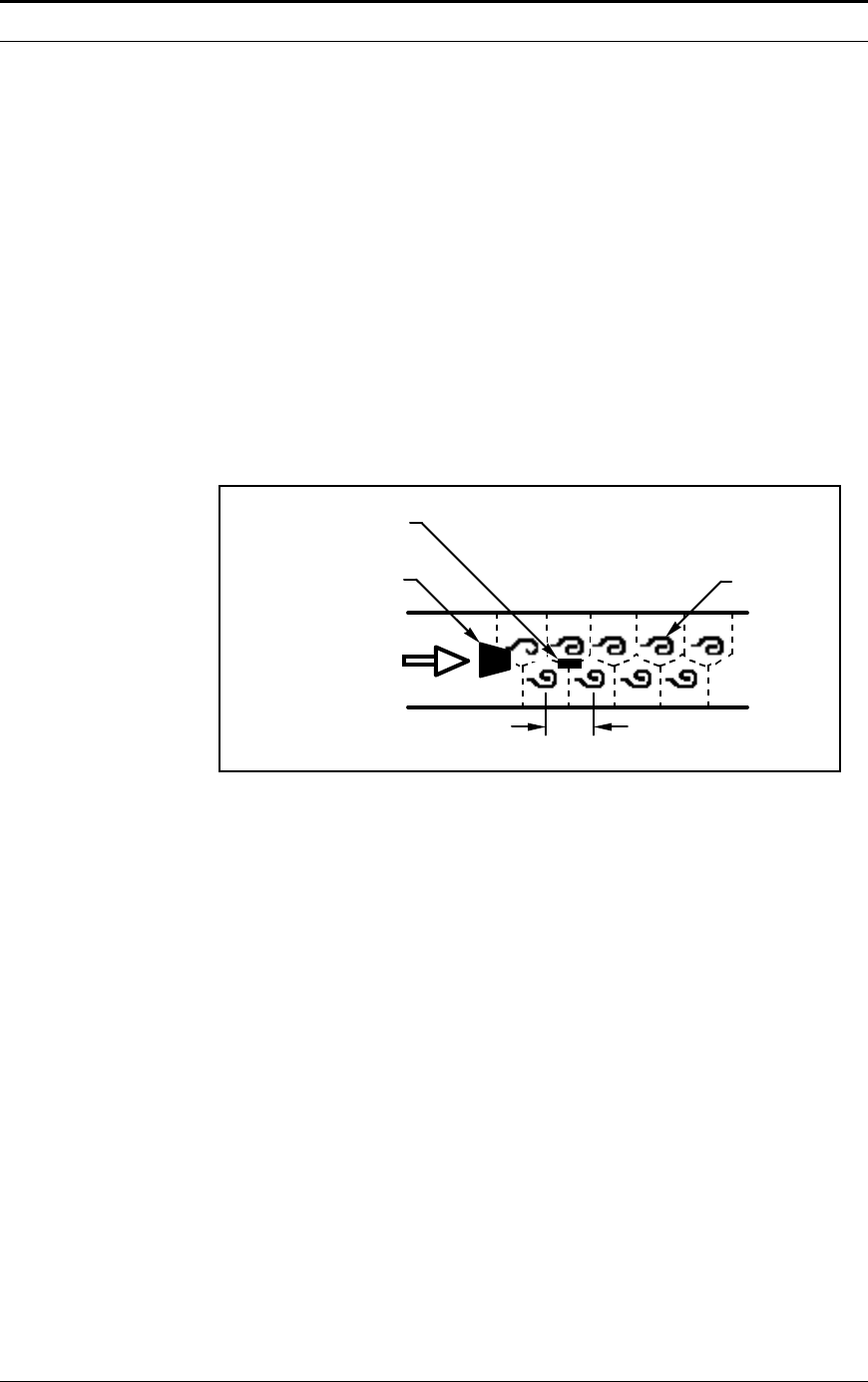
Vortex Shedding Frequency
Von Karman vortices form downstream of a shedder bar into two dis-
tinct wakes. The vortices of one wake rotate clockwise while those of
the other wake rotate counterclockwise. Vortices generate one at a time,
alternating from the left side to the right side of the shedder bar. Vortices
interact with their surrounding space by over-powering every other
nearby swirl on the verge of development. Close to the shedder bar, the
distance (or wave length) between vortices is always constant and meas-
urable. Therefore, the volume encompassed by each vortex remains con-
stant, as shown below. By sensing the number of vortices passing by the
velocity sensor, the Innova-Mass™ Flow Meter computes the total fluid
volume.
Vortex shedder bar
Flow
Vortices
Velocity sensor
Constant
wave length
Figure 1-2. Measurement Principle of Vortex Flow Meters
Vortex Frequency Sensing
The velocity sensor incorporates a piezoelectric element that senses the
vortex frequency. This element detects the alternating lift forces pro-
duced by the Von Karman vortices flowing downstream of the vortex
shedder bar. The alternating electric charge generated by the piezoelec-
tric element is processed by the transmitter’s electronic circuit to obtain
the vortex shedding frequency. The piezoelectric element is highly sensi-
tive and operates over a wide range of flows, pressures and temperatures.


















