E6581222
37
■ Relating communication parameters
Following parameters should be set or changed if necessary.
• Communication baud rate ()... Shipment setting = : 9600bps
Baud rate of all inverters in the network (master and slave) should be same network.
• Parity () ... Shipment setting = : Even parity
Parity of all inverters in the network (master and slave) should be same network.
• Communication error trip time() ... Shipment setting =
Operation is continued by the last received command value in the case of a communication break-
down. To stop the operation of inverter, provide a communication time-out interval (ex. =)
to the slave inverters. The master inverter does not trip even though the communication breakdown
happens. To trip the master inverter, provide an interlock mechanism by installing a FL fault relay
point or the like from the slave side.
• Frequency point selection ()
Adjusted to the system.
See chapter “6.1 Speed proportional control” for details.
■ Setting example of parameters
Parameters relating to the master side (example)
Master (transmission of output frequency
(%) (100% at FH))
Selection of communication protocol
(Toshiba inverter protocol)
Communication baud rate
(ex. 19200bps)
Parity (even parity)
Example: Panel
Example: Built-in potentiometer
Communication waiting time
(ex. 30msec)
Parameters relating to the slave side (example)
Slave (0Hz command issued in case the master inverter
fails)
Selection of communication protocol
(Toshiba inverter protocol)
Communication time-out (ex. 1 second)
Communication baud rate (same to the master side)
Parity (same to the master side)
Terminal block (ex. Driven by F, ST)
( Run and stop of operation is controlled with the frequency
reference value by setting the “run frequency”.)
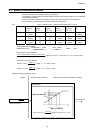
< For speed control >
Serial communication
? Adjusted to the system Point 1 setting (%)
? Ditto Point 2 frequency (Hz)
? Ditto Point 2 setting (%)
? Ditto Point 2 frequency (Hz)