20080201
The values of
a
and
b
depend on the scientific discipline, which can be specified by the
value of
n
(optional fourth parameter of Fourier and invFourier) as shown below.
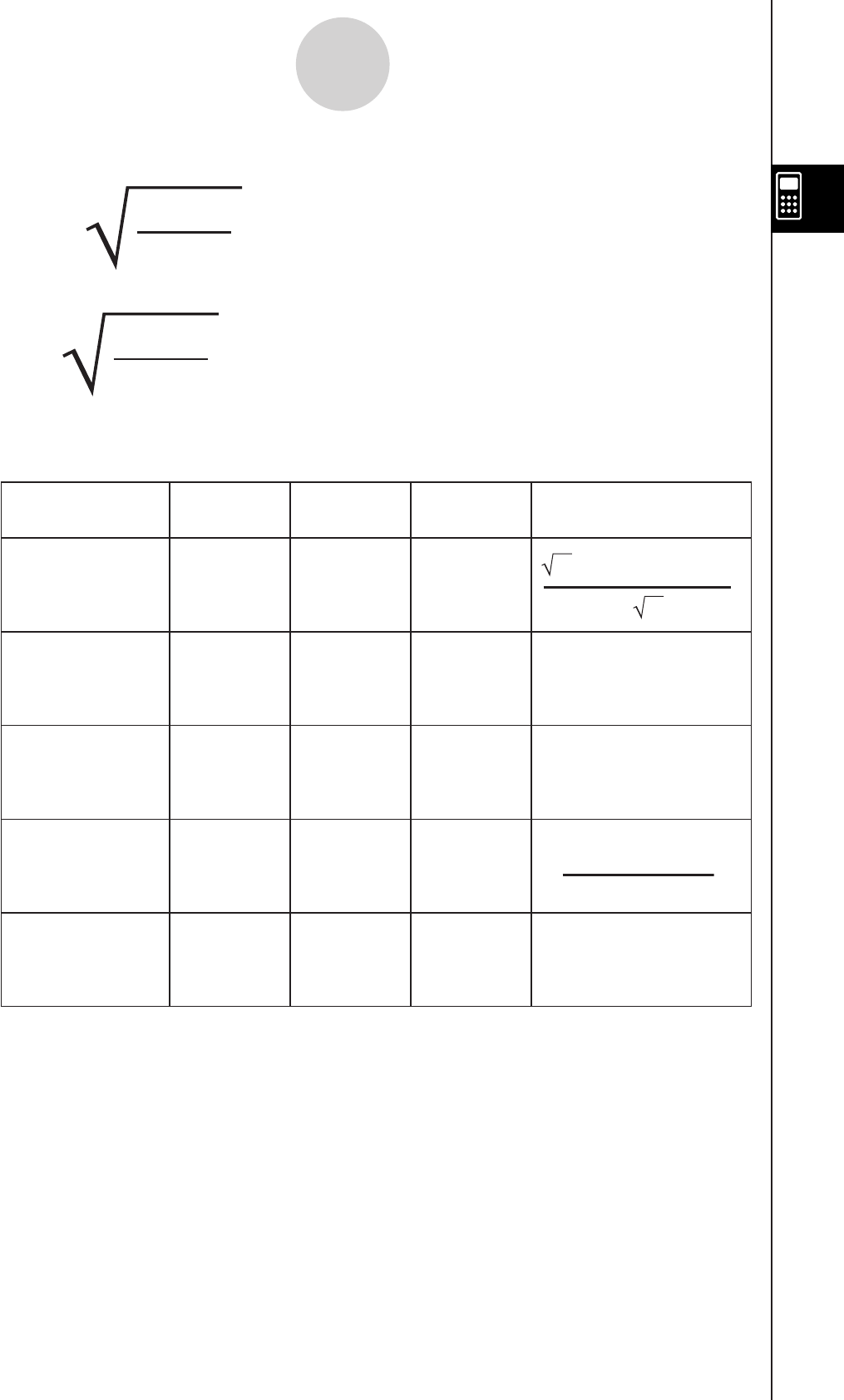
n
(optional)
ab
Definition of the Fourier
Integral
Modern Physics
001
∫
∞
–∞
e
ω•x•i
•
f(x)dx
2
•
2
•
π
Pure Math
11–1
Probability
211
Classical Physics
3–11
∫
∞
–∞
e
ω•x•i
•
f(x)dx
2
•
π
Signal Processing
4 0 –2*
π
Tip
• The Advanced Format dialog box can be used to configure settings related to the Fourier
Transform, such a Fourier Transform definition, etc. For details, see “Advanced Format Dialog
Box” on page 1-9-11.
2-8-10
Using the Action Menu
The Fourier Transform pairs are defined using two arbitrary constants
a
,
b
.
∫
∞
–∞
f(t)e
ibωt
dt
F(ω) =
⏐
b ⏐
(2
π)
1–a
∫
∞
–∞
F(ω)e
–ibωt
dω
f(t) =
⏐
b ⏐
(2
π)
1+a
∫
∞
–∞
e
–
ω•x•i
•
f(x)dx
∫
∞
–∞
e
ω•x•i
•
f(x)dx
∫
∞
–∞
e
–2•π•ω•x•i
•
f(x)d
x


















