1-4
Cisco H.323 Signaling Interface User Guide
OL-4806-01 Rev. A14
Chapter 1 Cisco H.323 Signaling Interface Overview
Operational Environment
RUDP
RUDP transports the E-ISUP messages between the PGW 2200 and the Cisco HSI.
RUDP is a Cisco proprietary, connection-oriented, packet-based transport protocol.
RADVision H.323
The Cisco HSI 4.1 release uses the RADVision 4.1 H.323 stack. The HSI uses the H.225 (Q.931 and
registration, admission, and status [RAS] protocol) and H.245 protocols to implement the H.323 gateway
signaling function.
RADVision H.323 enables the creation of real-time voice H.323 calls over IP networks.
E-ISUP
E-ISUP is a proprietary Cisco protocol based on ISUP. E-ISUP is used for inter-PGW 2200 call control.
E-ISUP uses a subset of ISUP messages. The main differences between ISUP and E-ISUP are as follows:
• E-ISUP is for the control of packet voice connection. It does not have circuit management messages
such as circuit reset and blocking.
• E-ISUP is transported over RUDP in an IP network.
• E-ISUP enables PGW 2200s to transport Session Description Protocol (SDP) information (such as
endpoint IP address and codec specifications) for call endpoints.
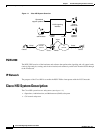
The Cisco HSI provides a conversion between the E-ISUP call control protocol originating from the
PGW 2200 and the H.323 call control protocol originating from the IP network (see
Figure 1-1).
New Features in Cisco HSI Release 4.1
The features introduced in the Cisco HSI 4.1 release are:
• Support of H.323 Version 4
• Invocation of Empty Capabilities Set
• Notify Support
• Disk Mirroring
• Additional security features
Operational Environment
This section provides operational environment requirements for the Cisco HSI.
Hardware Requirements
The hardware requirements for the Cisco HSI are documented in the Cisco Media Gateway Controller
Hardware Installation Guide. See the section “Cisco MGC Host Platforms” in Chapter 1.