1344 Managing IPv4 and IPv6 Multicast
candidate RPs to all the PIM routers in the network. Each PIM router then
runs the RP selection algorithm to determine an RP for the given group
range. All the interested PIMSM routers then initiate re-reception of traffic
through this new RP, and the multicast traffic is rerouted via the new RP. This
is to provide high availability to the multicast applications and help ensure
that the multicast traffic is recovered quickly in such scenarios.
PIM-SM Protocol Operation
This section describes the workings of PIM-SM protocol per RFC 4601. The
protocol operates essentially in three phases, as explained in the following
sections.
Phase-1: RP Tree
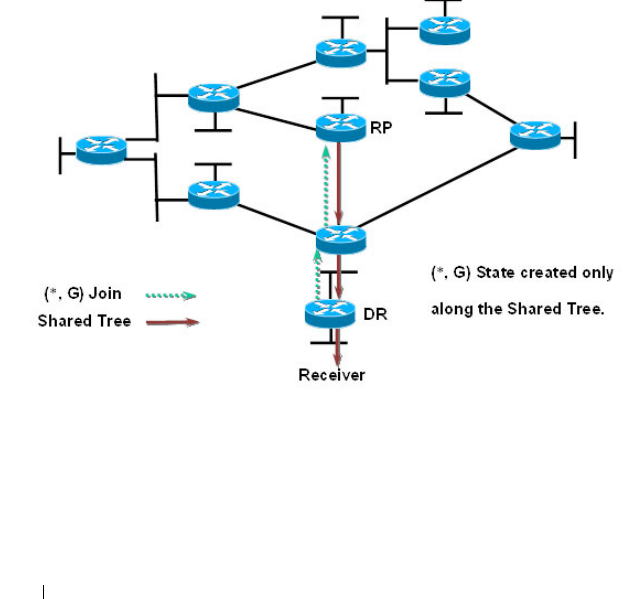
Figure 43-1. PIM-SM Shared Tree Join
• In this example, an active receiver (attached to leaf router at the bottom of
the drawing) has joined multicast group “G”.
• The leaf router (labeled DR above) knows the IP address of the
Rendezvous Point (RP) for group G and sends a (*, G) Join for this group
towards the RP.


















