Chapter 4: Web Configuration
101
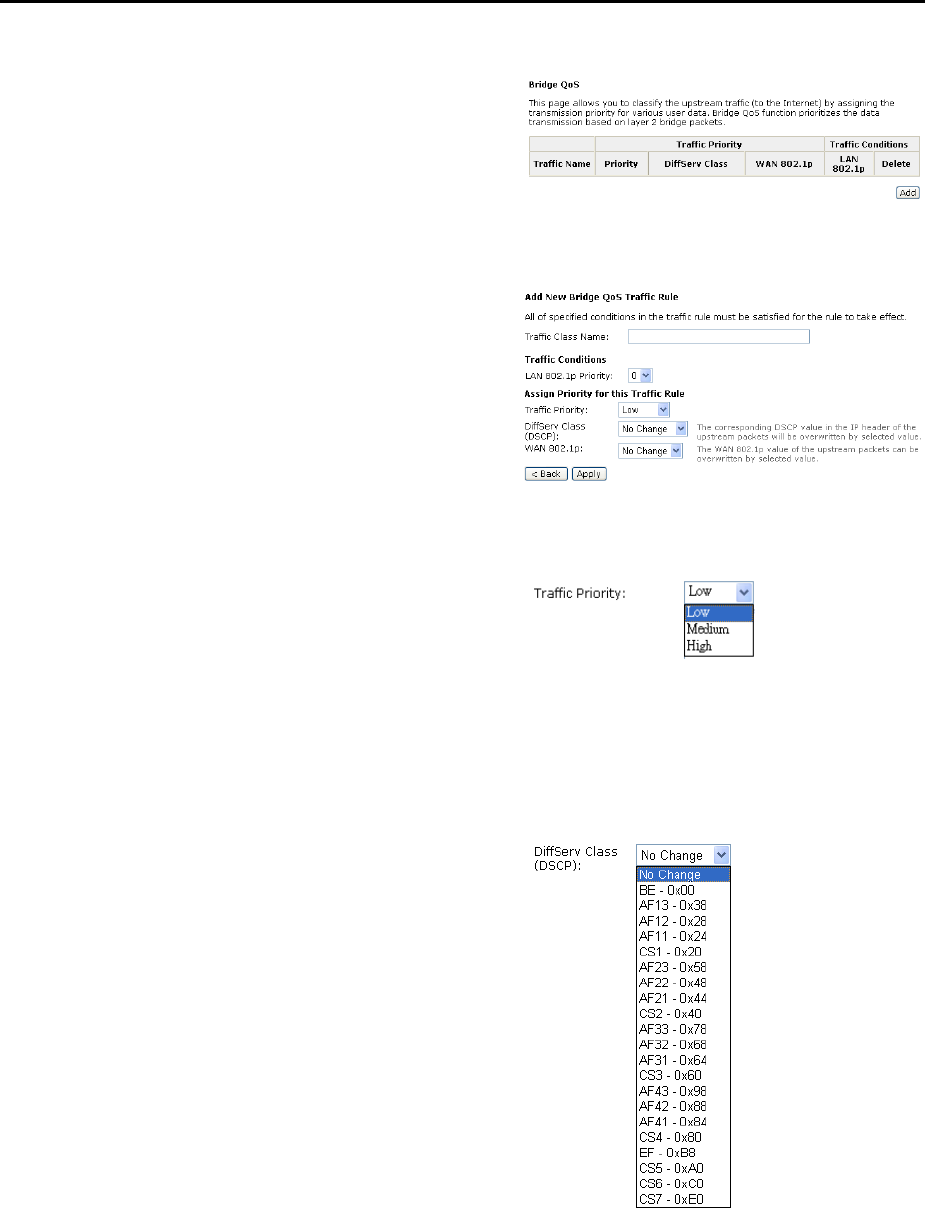
Quality of Service – Bridge QoS
To classify the upstream traffic by
assigning the transmission priority for
different users’ data, please use
Bridge QoS to prioritize the data
transmission.
The Bridge QoS allows you to set the
settings based on layer two bridge
packets.
Traffic Class Name:
Key in a name as the traffic class for
identification.
802.1p Priority:
Each incoming packet will be mapped
to a specific priority level, so that
these levels may be acted on
individually to deliver traffic
differentiation. Please choose the
number (from 0 to 7, low to high
priority) for the 802.1p Priority.
Traffic Priority:
There are three options – Low,
Medium, and High that you can
choose. The IAD will arrange the
precedence for the traffic according to
the traffic priority setting here.
As for the settings for the DSCP value
and the WAN 802.1p value of the
upstream packets, they will be seen
on the WAN side.
DiffServ Class (DSCP):
DiffServ is a computer networking
architecture that specifies a simple,
scalable and coarse-grained
mechanism for classifying, managing
network traffic and providing QoS
(quality of service) guarantees on
modern IP networks. DiffServ can, for
example, be used to provide
low-latency, guaranteed service to
critical network traffic such as voice or
video while providing simple best-effort
traffic guarantees to non-critical
services such as web traffic or file
transfers.
The higher position the item appears,
the smaller DSCP value it is (i.e., BE
is the lowest while CS7 is the highest).
The corresponding DSCP value in the
IP header of the upstream packets will
be overwritten by the selected value.
The default setting is No change.


















