Wireless IAD User Manual
124
Definitions of FXS and FXO
FXS (Foreign eXchange Subscriber) interface delivers POTS service from the local
phone company and connects to subscriber equipment (e.g., phone, fax, modem..
and so on). That is, an FXS interface will point to the subscriber directly. An FXS
interface can provide primary service of dial tone, battery current and ring voltage to
a subscriber device.
FXO (Foreign eXchange Office) interface receives POTS service, from a central CO
of PSTN. That is, an FXO interface will point to the Telco office directly. An FXO
interface can provide primary service of on-hook/off-hook indication to the Telco
network device.
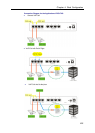
The following illustration shows the hardware connection for the FXS and FXO
interfaces.
Call procedure of FXS-FXO
The call procedure for FXS and FXO differs for each other. Refer to the following for
reference.
For the side of FXS: For the side of FXO:
z Initiating a call by
Presenting ring voltage over the
line to the attached FXO device.
(Notice that the FXS device
cannot pass dialed digits.)
z Initiating a call by
Going off-hook to seize the
telephone line and
Dialing the dual-tone
multi-frequency (DTMF) digits that
can identify the destination to be
called.
z Receiving a call by
Detecting the line that has been
seized (the attached
telephone-FXO device-has gone
off hook)
and
Receiving dual-tone
multi-frequency (DTMF) digits
indicating how the call should be
routed.
z Receiving a call by
Detecting the ring voltage supplied
by the FAX device
and
Going off-hook to answer the call.
Notice that the FXS devices will supply DC power to the line.