MAN607-S
28-03-2003 Page 2-14 of 53
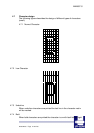
64 through 256 dots can, however, are set using the command for setting
the number of dynamic division dots.
When the maximum number of activated dots is 128 dots, and all of the
dots are driven, as shown in
2.6.6 Head Control Circuit
The PRN607-S has a function for measuring the resistance of the thermal
head connected to the FTP607MCLxxx.
The PRN607-S measures the resistance of the thermal head and detects
the errors at initialisation.
Based on the measurement, the PRN607-S determines how much energy
to apply. No adjustment is needed for replacing the FTP607MCLxxx to get
the best printing.
2.6.7 Head temperature measurement circuit
The thermistor is mounted on the FTP607MCLxxx to measure the
temperature of the thermal head.
The PRN607-S determines the energy to be applied to the head and also
checks for head temperature errors.
If the temperature of the thermal head is -10 °C or lower, or 80 °C or higher,
the PRN607-S stops driving and puts the printer in head temperature error
status. If the temperature of the thermal head is returned to from -5 °C to 75
°C, the printer goes to printable status.
2.6.8 Vhead interrupt circuit
This circuit interrupts Vhead to prevent electrolytic corrosion of the thermal
head and to enable the detection of the resistance mentioned above.
Electrolytic corrosion may significantly shorten the life of the thermal head.
Thermal paper ordinarily contains electrolytic material to prevent sheets
from sticking to each other due to static electricity. If there is too much of
this electrolytic material, high temperatures and humidity cause the material
to ionise, resulting in electrolytic corrosion of the thermal head.
The PRN607-S turns the FET off and breaks the Vhead applied to the
thermal head during waiting status to prevent electrolysis corrosion of the
thermal head.