Chapter 2. Components 23
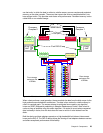
use fast-write, in which the data is written to volatile memory on one complex and persistent
memory on the other complex. The server then reports the write as complete before it has
been written to disk. This provides much faster write performance. Persistent memory is also
called NVS or non-volatile storage.
Figure 2-3 DS8000 architecture
When a host performs a read operation, the servers fetch the data from the disk arrays via the
high performance switched disk architecture. The data is then cached in volatile memory in
case it is required again. The servers attempt to anticipate future reads by an algorithm
known as SARC (Sequential prefetching in Adaptive Replacement Cache
). Data is held in
cache as long as possible using this smart algorithm. If a cache hit occurs where requested
data is already in cache, then the host does not have to wait for it to be fetched from the
disks.
Both the device and host adapters operate on a high bandwidth fault-tolerant interconnect
known as the RIO-G. The RIO-G design allows the sharing of host adapters between servers
and offers exceptional performance and reliability.
SAN fabric
Processor
Complex 0
Processor
Complex 1
Fibre channel switch
Front storage
enclosure with
16 DDMs
Rear storage
enclosure with
16 DDMs
Fibre channel switch
Fibre channel switch
Fibre channel switch
Persistent memory
Volatile
memory
N-way
SMP
Persistent memory
Volatile
memory
N-way
SMP
RIO-G
RIO-G
First RIO-G loop
Device adapter
Device adapter
Host adapter
in I/O enclosure
in I/O enclosure
in I/O enclosure
Host adapter
in I/O enclosure
Host ports