Chapter 2. Components 33
These problems are solved with the
switched FC-AL implementation on the DS8000.
Switched FC-AL advantages
The DS8000 uses switched FC-AL technology to link the device adapter (DA) pairs and the
DDMs. Switched FC-AL uses the standard FC-AL protocol, but the physical implementation is
different. The key features of switched FC-AL technology are:
Standard FC-AL communication protocol from DA to DDMs.
Direct point-to-point links are established between DA and DDM.
Isolation capabilities in case of DDM failures, providing easy problem determination.
Predictive failure statistics.
Simplified expansion; for example, no cable re-routing is required when adding another
disk enclosure.
The DS8000 architecture employs dual redundant switched FC-AL access to each of the disk
enclosures. The key benefits of doing this are:
Two independent networks to access the disk enclosures.
Four access paths to each DDM.
Each device adapter port operates independently.
Double the bandwidth over traditional FC-AL loop implementations.
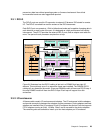
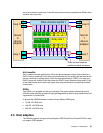
In Figure 2-11 each DDM is depicted as being attached to two separate Fibre Channel
switches. This means that with two device adapters, we have four effective data paths to each
disk, each path operating at 2Gb/sec. Note that this diagram shows one switched disk
network attached to each DA. Each DA can actually support two switched networks.
Figure 2-11 DS8000 disk enclosure
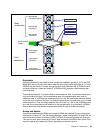
When a connection is made between the device adapter and a disk, the connection is a
switched connection that uses arbitrated loop protocol. This means that a mini-loop is created
between the device adapter and the disk. Figure 2-12 on page 34 depicts four simultaneous
and independent connections, one from each device adapter port.
server 0
device
adapter
server 1
device
adapter
Fibre channel switch
Fibre channel switch