32 DS8000 Series: Concepts and Architecture
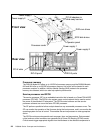
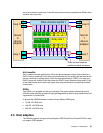
Figure 2-9 DS8000 disk enclosure
Non-switched FC-AL drawbacks
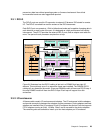
In a standard FC-AL disk enclosure all of the disks are arranged in a loop, as depicted in
Figure 2-10. This loop-based architecture means that data flows through all disks before
arriving at either end of the device adapter (shown here as the
Storage Server).
Figure 2-10 Industry standard FC-AL disk enclosure
The main problems with standard FC-AL access to DDMs are:
The full loop is required to participate in data transfer. Full discovery of the loop via LIP
(loop initialization protocol) is required before any data transfer. Loop stability can be
affected by DDM failures.
In the event of a disk failure, it can be difficult to identify the cause of a loop breakage,
leading to complex problem determination.
There is a performance dropoff when the number of devices in the loop increases.
To expand the loop it is normally necessary to partially open it. If mistakes are made, a
complete loop outage can result.