$msg = PRINTF("Job %s for user %s is on message wait", $F1, $F2);
END
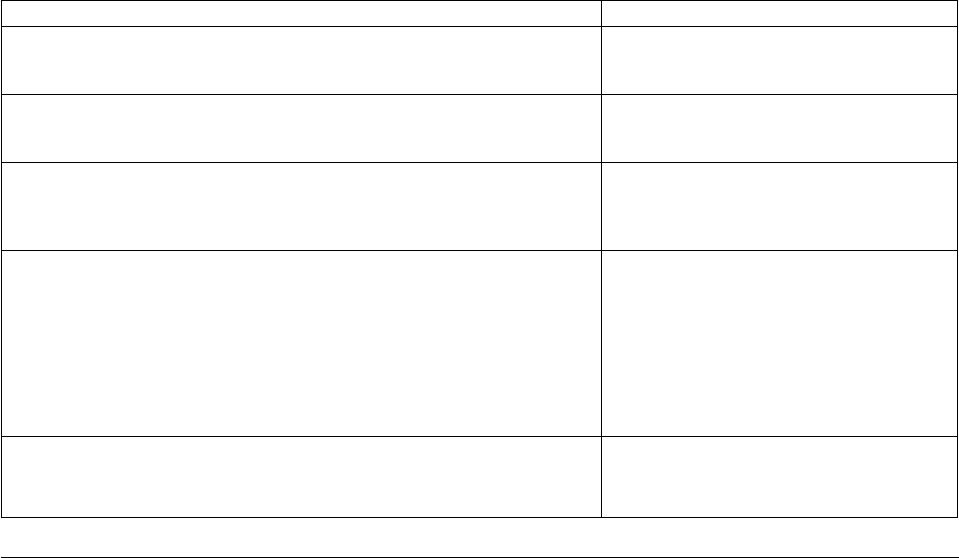
Table 3 describes each statement in the example:
Table 3. Explanation of operators in example code
Code Explanation
SELECT
ATTR(=,$MSG), VALUE(PREFIX,"Job");
A match occurs when any message arriving
with the Class=AS400_MSG, where the first
part of the message field equals Job.
SELECT
ATTR(=,$MSG), VALUE(CONTAINS,"for User");
A match occurs when the message field
contains for User anywhere within the
message text.
SELECT
ATTR(=,$MSG), VALUE(SUFFIX,"You must investigate.");
In order to match, the end of the message field
must be the text You must investigate. The
case of the message must be exactly as shown
in the example.
FETCH
SUBSTR($MSG,4,8)
SUBSTR($MSG,22,8)
This part of the FETCH statement pulls
characters from the message field. It starts at
character 5, because it is zero-based. It pulls a
total of eight characters. For example, the
message is Job 12345678 for User stephens
has stopped. You must investigate. The
statement pulls 12345678 for the first line of the
FETCH statement. The second line pulls the
text stephens.
MAP
$severity = CRITICAL;
$msg = PRINTF("Job %s for user %s is on message wait", $F1, $F2);
The severity attribute is set to CRITICAL. It
prints using the two items that were pulled
with the FETCH statement.
Class Definition Statement File Details
For each class of event supported by an adapter, one or more class definition
statements are present in the CDS file. These statements define which incoming
event maps to a particular class and how the attributes of the formatted event
instance going to the event server are filled with values. The class definition
statements are described as follows:
SELECT
Specifies the criteria an incoming event must satisfy to match a class.
FETCH
Retrieves data from the incoming event that is necessary to fill the attribute
values.
MAP Specifies how to fill attribute values for an event instance from data
retrieved by FETCH statements.
Class definition statements are evaluated in the order they appear in the CDS file.
An incoming event is mapped to the class specified by the first class definition
statement whose SELECT statement is evaluated successfully.
When more than one class definition statement is provided for a particular class of
event, the class definition statement with the most restrictive SELECT statement is
placed before the less restrictive statements in the CDS file. Locating the most
restrictive class definition statement first for a same-named class provides for
better performance of the adapter.
156 IBM Tivoli Enterprise Console: Adapters Guide


















