- 16 -
2.4.4 Port Controls
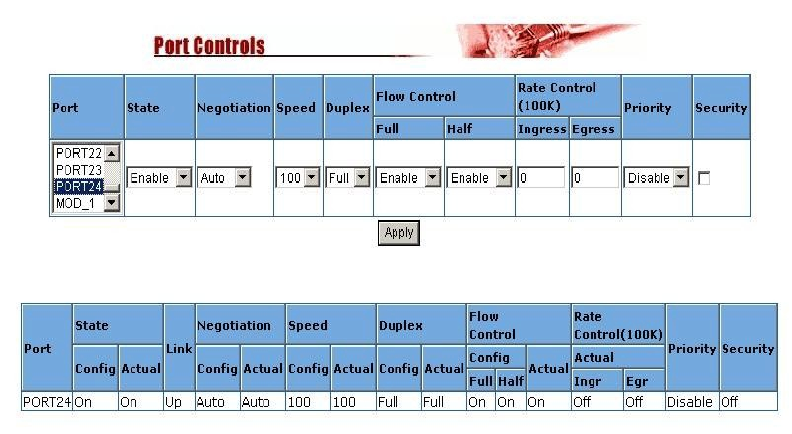
The Port Controls page allows the user to modify the operational mode of each port.
1. State: Used to enable or disable this port.
2. Auto Negotiation: Used to set the auto-negotiation mode.
Settings are: Auto, Nway and Forced.
# Auto instructs the switch to learn the parameters of the device connected.
# Nway instructs the switch to use the Nway protocol to instruct devices
connected to the port of its defined parameters. (Speed and Duplex should be
defined)
# Forced does not negotiate with the connected device its parameters.
3. Speed: Used to set the port speed to either 100Mbps or 10Mbps on
Port1~Port24. 1000Mbps, 100Mbps or 10Mbps speed on Port25 and Port26
(depending on module card used).
4. Duplex: Used to set full-duplex or half-duplex mode of the port
5. Flow control:
Full: Used to enable or disable flow control when in full duplex mode.
Half: Used to enable or disable backpressure flow control when in half duplex
mode.
6. Rate Control: Ports1 ~ port 24, support ingress and egress rate control (inwards
and outwards). For example, assume that port 1 is connected at 10Mbps. The
switch administrator could set the effective port throughput levels by using the
Rate Control function on that port to 1Mbps egress (outwards) and 500Kbps
ingress (inwards). An example of where to use this could possibly be to limit the
Internet bandwidth to a FTP server.
The switch will perform full duplex flow control or half duplex backpressure flow
control to confine the port speeds to match specified ingress/egress rates.
Ingress: Specify the ports effective ingress rate. Valid range is 0 ~ 1000.
The unit is 100K.
0: disable rate control.
Egress: Specify the ports effective egress rate. Valid range is 0~1000.
The unit is 100K.
0: disable rate control.


















