- 73 -
5.0 Application Examples:
5.1 VLAN applications used with switch.
A VLAN is a simple option to protect your network against broadcast storms by
creating segments based on Layer2 Ethernet information. It avoids the complexity
and heavy processing requirements of Layer3 IP based routers, while providing
some similar functionality.
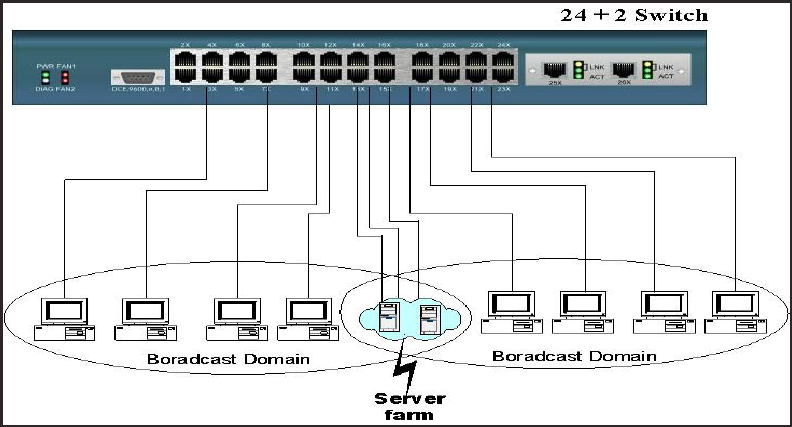
Each VLAN grouping forms a separate isolated Broadcast Domain. These Domains
(VLAN’s) can overlap to allow multiple VLAN groups to access servers, which need
to exist in all VLAN groups.
Virtual LAN, or VLAN’s should be created where broadcast traffic needs to be limited
to within certain groupings of nodes. Adding VLAN’s will improve the efficiency of
your network, as individual PC’s will receive and respond to fewer broadcast packets.
They also provide security, by not forwarding packets between VLAN’s.
Example: You have 2 serviced offices within one building. 2 companies operate from
the one building. You want to allow both to use the Internet via your site proxy server,
but do not want the PC’s in one office to be able to connect to any of the PC’s in the
other office. If you grouped the 2 offices in their own VLAN’s, and then grouped the
proxy server in both VLAN’s, you have secured the site.
Benefits of VLAN’s
• Grouping users into logical networks for performance enhancement.
• Provides effective broadcast containment between segmented ports, this can
prevent network broadcast flooding issues.
• Offers security by completely isolating different Broadcast Domains.
• Can preserve existing investment in equipment and cabling.
• Provides an easy, flexible, and economic way to modify users into groups as
needed.
• Network administrators can easily "fine tune" the network.
• Separates network structure from the physical topology of the cabling.
• Makes large networks more manageable.


















