- 17 -
7. Port Priority: This is used to force any non prioritised packets to either High, Low,
or Disabled states.
8. Port Security: Setting a ports security mode to on (by ticking the check box) will
lock it to all unauthorized MAC addresses. This disables the address learning
functionality on the port and then only incoming packets with a known source MAC
addresses will be forwarded by the port. Administrators can disable the port from
learning any new MAC addresses, and then use the static MAC addresses table
entry screen to define a list of MAC addresses that can be used by the secure
port.
2.4.5 Trunking
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a standardised means for
exchanging information between Partner Systems that require high-speed redundant
links. Link aggregation lets you group up to eight consecutive ports into a single
dedicated connection. This feature can expand bandwidth to a device on the
network. LACP operation requires full-duplex mode, more detail information refers
to the IEEE 802.3ad standard.
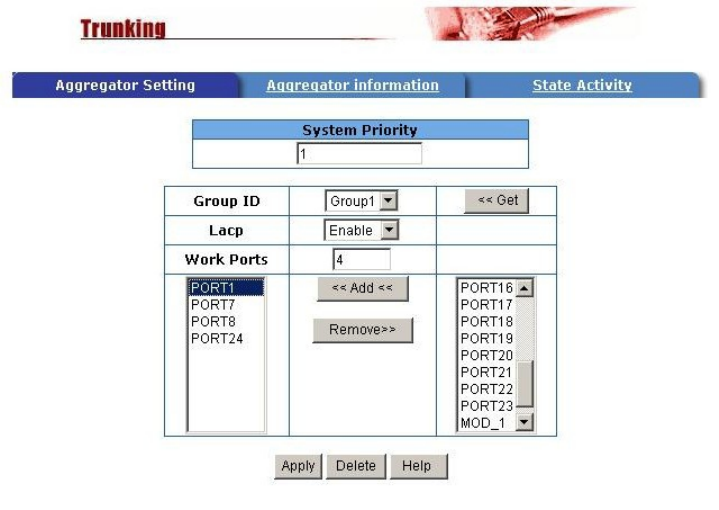
2.4.5.1 Aggregator setting
Link aggregation lets you group up to 4 consecutive ports into a single dedicated
connection. This feature can expand bandwidth to a device on the network, such as
another switch or a server, and also provide redundancy features.
1. System Priority: A value used to identify the active LACP. The switch with the
lowest value has the highest priority and is selected as the active LACP.
2. Group ID: There are seven trunk groups provided. Choose the "group id" and
click "Get" to display the group settings.
3. LACP: If enabled, the group defined in the ‘Work Ports’ is a LACP static trunking
group. If disabled, the group is a LOCAL static trunking group (not LACP aware).
By default all ports support LACP dynamic trunking. If the switch is connecting to a
device that also supports LACP, then the LACP dynamic trunking group will be
created automatically.


















