51
6-2 Reducing Response Time (C200H, C200HS,
C200HX/HG/HE(-Z))
IORF(97) can be used in programming to shorten the I/O response time
greater than is possible by setting a high number of refresh bits. (Remember,
increasing the number of refresh bits set on the back-panel LED shortens
response time, but increases the scan time of the PC.) The following calcula-
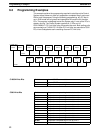
tions for the maximum scan time use the same example System configura-
tion as that used in 6-1 Response Times. In programming the PCs for PC
Link Units #0 and #7, IORF(97) is executed during every PC scan for the PC
Link Units. The basic equation for the maximum I/O response time is as fol-
lows:
Response time = input ON delay + [scan time of PC of Unit 0 x (number of
LR transfer bits ÷ number of I/O refresh bits ÷ 2)] + alpha +
PC Link scan time + invitation sequence processing time +
{scan time of PC of Unit 7 x [(number of LR transfer bits ÷
number of I/O refresh bits ÷ 2) x 2 + 1]} + beta + output ON
delay
If scan time of PC of Unit 0 > PC Link scan time, alpha = scan time of PC of
Unit 0. If scan time of PC of Unit 0 < PC Link scan time, alpha = PC Link
scan time.
If scan time of PC of Unit 7 > PC Link scan time, beta = scan time of PC of
Unit 7. If scan time of PC of Unit 7 < PC Link scan time, beta = PC Link scan
time.
The required data from the example System configuration is as follows:
Input ON delay 1.5 ms
Output ON delay 15 ms
Scan time of PC of Unit 0 20 ms + 5.7 ms = 25.7
(required for IORF execution)
Scan time of PC of Unit 7 50 ms + 5.7 ms = 55.7
(required for IORF execution)
Number of PC Link Units 8
Number of LR bits 1,024
Number of refresh bits for Unit 0 256
Number of refresh bits for Unit 7 256
PC Link scan time 32.4 ms
Invitation sequence processing time 0 ms
Placing these values into the equation produces a maximum I/O response
time of 466.9 ms, approximately 200 ms shorter than that obtained for the
same I/O example in 6-1 Response Times.
Reducing Response Time (C200H, C200HS, C200HX/HG/HE/(-Z)) Section 6-2