2-229
2 Instructions
CP1E CPU Unit Instructions Reference Manual(W483)
Floating-point Math
Instructions
2
Floating-point Math Instructions
The Floating-point Math Instructions convert data and perform floating-point arithmetic operations.
Data Format
Floating-point data expresses real numbers using a sign, exponent, and mantissa. When data is
expressed in floating-point format, the following formula applies.
Real number = (–1)
s
2
e–
127
(1.f)
s: Sign
e: Exponent
f: Mantissa
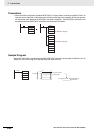
The floating-point data format conforms to the IEEE754 standards. Data is expressed in 32 bits, as follows:
Number of Digits
The number of effective digits for floating-point data is seven digits for decimal.
Floating-point Data
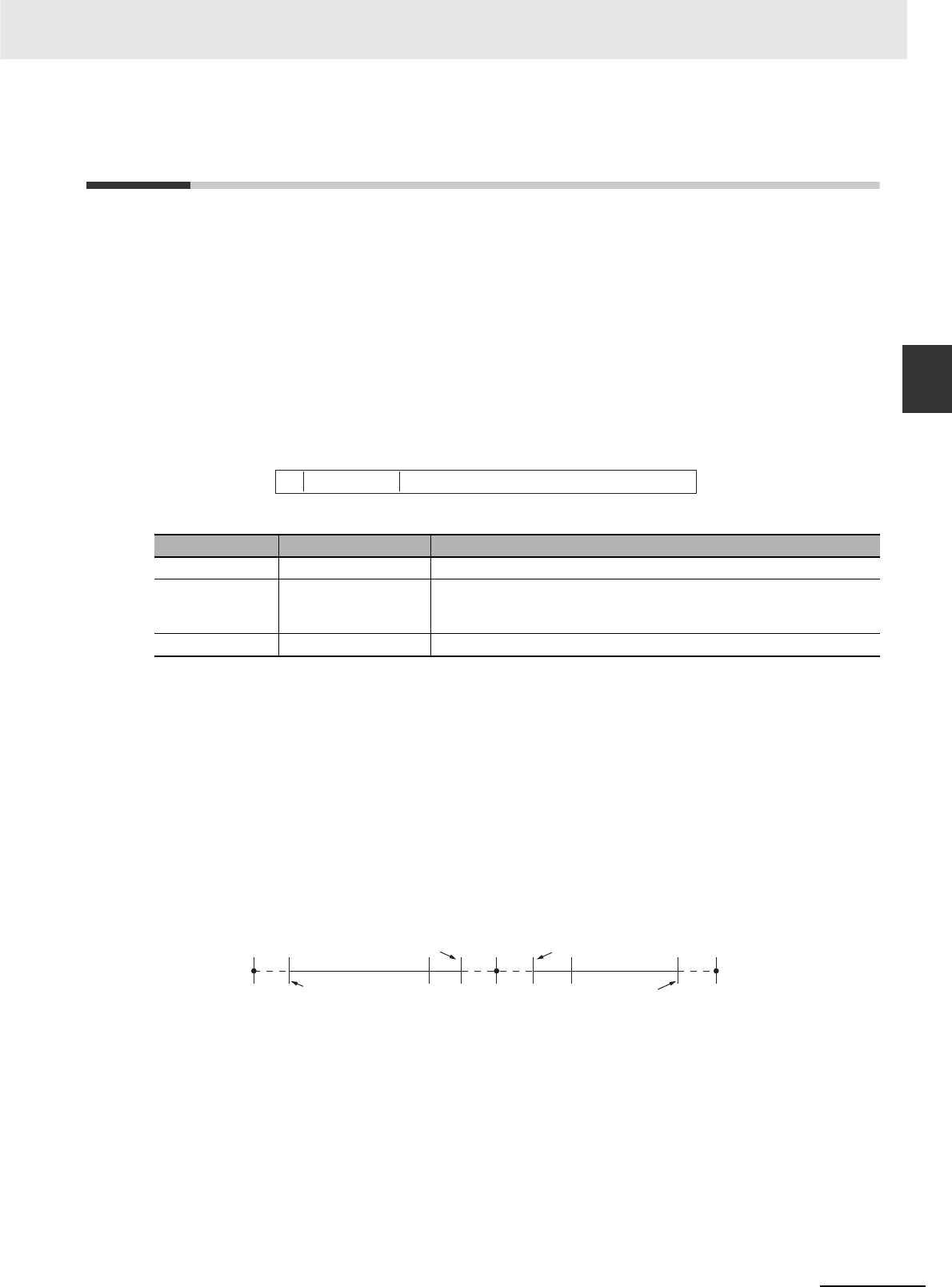
The following data can be expressed by floating-point data:
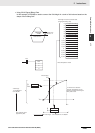
• –∞
• –3.402823 × 10
38
≤ value ≤ –1.175494 × 10
–
38
• 0
• 1.175494 × 10
–
38
≤ value ≤ 3.402823 × 10
38
• +∞
• Not a number (NaN)
Special Numbers
The formats for NaN, ±∞, and 0 are as follows:
• NaN*:e = 255, f ≠ 0
• +∞:e = 255, f = 0, s= 0
• –∞:e = 255, f = 0, s= 1
• 0: e = 0, f = 0
* NaN (not a number) is not a valid floating-point number. Executing floating-point calculation instructions will not
result in NaN.
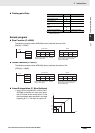
Data No. of bits Contents
s: sign 1 0: positive; 1: negative
e: exponent 8 The exponent (e) value ranges from 0 to 255. The actual exponent is the
value remaining after 127 is subtracted from e, resulting in a range of
–127 to 128. “e=0” and “e=255” express special numbers.
f: mantissa 23 The mantissa portion of binary floating-point data fits the formal 2.0 > 1.f ≥1.0.
es
f
31 30 23 22
0
Sign Exponent Mantissa
–1.175494 × 10
–38
1.175494 × 10
–38
– ∞
+ ∞
–3.402823 × 10
38
3.402823 × 10
38
–1
0
1